SIM-Cloud 5.0¶
The release of SIM-Cloud 5.0 is planned for the first half of 2021. The new version will bring significant improvements to the service, with changes that will affect practically all internal microservices of the platform.
Work on the new release is at the stage of active introduction; the following changes are already available to users:
1. Update of Horizon to the Rocky version (v.14.1.0)

Date of update: 8 February 2021
Main changes:
Generic Cinder groups are now supported.
Addition of server groups and quota management for server group participants.
Addition of Angularized Users and Server Groups panels to provide improved UX.
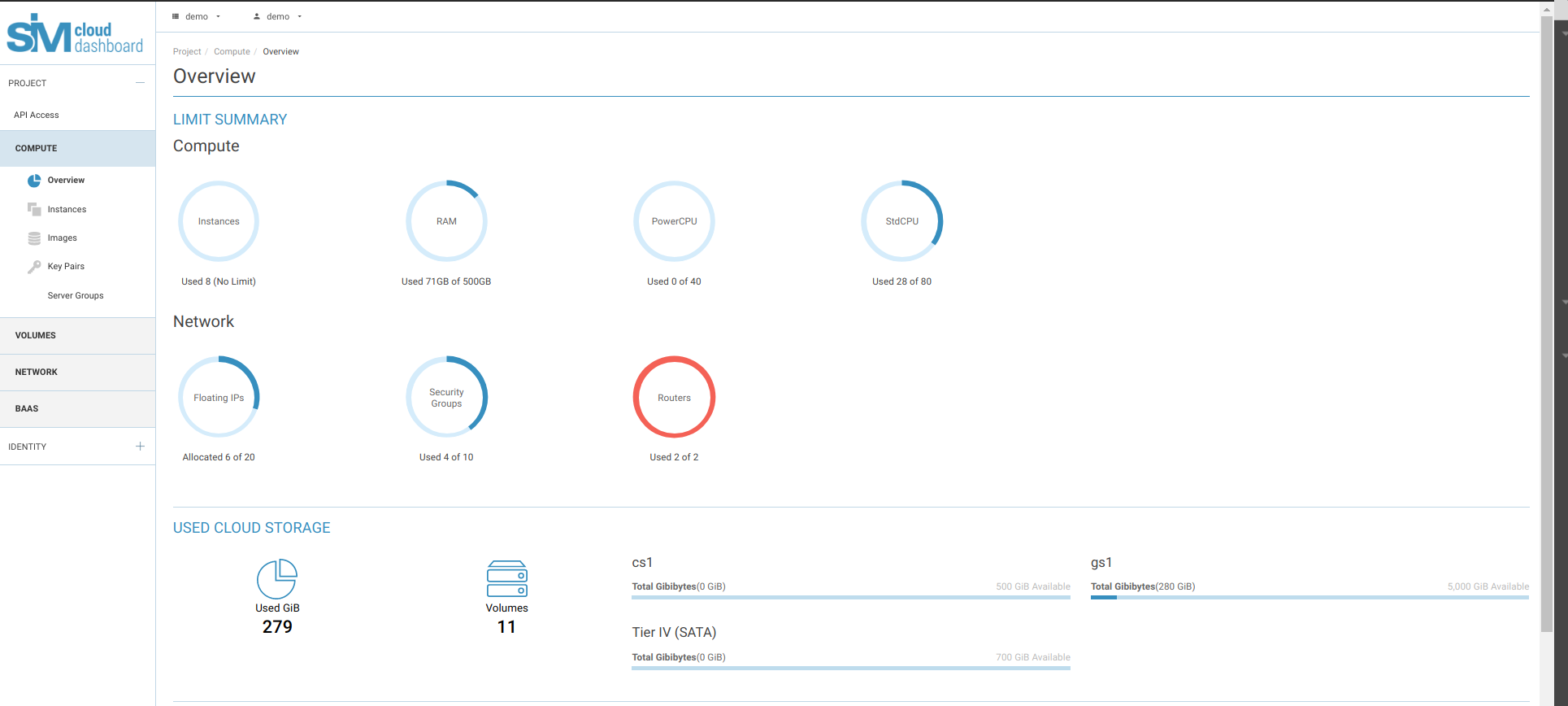
Changes to graphical display of available project resources on the Overview page. Change to grouping of Compute and Network resources.
Addition of Instances menu item to enable management of instance network interfaces.
The full list of changes is given in the official release from OpenStack
2. Update of Cinder to the Rocky version (v.13.0.9)

Date of update: 1 February 2021
Main changes:
- Improved user interaction for recoveries following failures in the storage system.
- Includes security improvements when creating volumes from signed images.
- Numerous improvements giving administrators greater control over the placement of volumes.
- Improved backup functionality and efficiency.
The full list of changes is given in the official release from OpenStack
3. Update of Nova to the Rocky version (v.18.3.0)
Date of update: 21 January 2021
Main changes:
- Improvements introduced to minimise network downtimes during dynamic migration. Additionally, the libvirt driver can now perform migration in real time between different types of network server, e.g. linuxbridge => OVS.
- Improved load processing from copies of a volume when there is insufficient local storage on the Nova computing node.
- Operators can now deactivate a cell to be certain that no new copies are planned in it. This is useful for operators when introducing new cells during deployment and for managing existing cells.
- Increased security when using images signed with Glance with the computing driver libvirt.
- A command, nova-manage db purge, is now available to aid the operator in maintaining databases and preventing bloating.
- The placement service now supports detailed configuration of the RBAC policy rules. For detailed information see the documentation on the placement policy.
The full list of changes is given in the official release from OpenStack
4. Update of Neutron to the Rocky version (v.13.0.7)

Date of update: 24 November 2020.
Main changes:
- Support for TCP / UDP port forwarding to floating IPs. Operators can store a quantity of global IP addresses for floating IP addresses.
- Supports a number of bindings for ports associated with a calculation, for improved support of server migration in real time.
- The filter parameters can be checked in the resources listing. The filter parameters were previously unknown to API users. In this release, the performance of API in the filtration of resources has been improved and many links provided to the documentation in the Neutron API.
- (fwaas) Supports firewall event registration. Useful for operators in debugging FWaaS.
- (vpnaas) Supports newer versions liberswan 3.19+, so operators can launch neutron-vpnaas IPsec VPN with more recent distributions.
- (ovn) Support for migration from existing ML2OVS TripleO deployment to ML2OVN TripleO deployment.
- (bagpipe) bagpipe-bgp, reference implementation of Neutron BGP VPN support, supports E-VPN with OVS.
The full list of changes is given in the official release from OpenStack
5. OS images updated
Date of update: 16 November 2020.
Main changes:
An annual project for updating the images in SIM-Cloud has been completed. Our team accomplished a major work on the preparation of images: MS Windows, Linux images, Virtual router/firewall, Virtual appliance, and this means that our cloud clients can use up-to-date software with the latest security updates, so guaranteeing them reliable working.
| Updated images |
|---|
| debian-10.5.1-20200830-openstack-amd64 |
| debian-9.13.3-20200910-openstack-amd64 |
| CentOS-8-GenericCloud-8.2 |
| CentOS-7-x86_64-GenericCloud-2003 |
| CentOS-6-x86_64-GenericCloud-1907 |
| Xenial-server-cloudimg-amd64 16.04 |
| Bionic-server-cloudimg-amd64 18.04 |
| Focal-server-cloudimg-amd64 20.04 |
| openSUSE-Leap-15.2-OpenStack.x86_64-Build8.25 |
| Fedora-Cloud-Base-32-1.6.x86_64 |
| Windows_2019_DatacenterEval_EN-DE-RU_1809 |
| Windows_2019_StandardEval_EN-DE-RU_1809 |
| Windows_2016_StandardEval_EN-DE-RU_1705 |
| Windows_2016_DatacenterEval_EN-DE-RU_1705 |
| Windows_2012R2_StandardEval_EN-DE-RU_9600 |
| Windows_2012R2_DatacenterEval_EN-DE-RU_9600 |
| Windows_10_EnterpriseLTSC_Eval_EN-DE-RU_1809 |
| FortiOS_v6.4.3 |
| OpnSense20.7 |
| CHR 6.46.7 (Long-term) RouterOS |
| PfSense2.4.5 |
| Cisco_asav9-14-1-30 |
| Kerio-control-appliance-9.3.5 |
| junos-media-vsrx-x86-64-vmdisk-20.2R1.10 |
| junos-media-vsrx-x86-64-vmdisk-18.4R3.3 |
| VMBitrix7.4-3-CentOS7.7-x86_64 |
The full list of images available is given in our article OS Images
6. Update of Glance to the Rocky version (v.17.0.0)

Date of update: 05 October 2020
Main changes:
- Support for a secure hashing algorithm that allows operators to set up a secure hash with self-description that can be used by image consumers to check the integrity of image data.
- Introduction of ‘hidden’ images, a popular request of operators, which enables operators to hide out-of-date, generally accessible images in response to the default image list, yet to remain available for recovery of the server
- The glance-manage utility has been updated, taking into account the remarks about the security of OpenStack OSSN-0075.
- Implementation of support for several server modules that enables operators to configure multiple storages and allows the end user to send image data to a specific storage, is presented as an EXPERIMENTAL API image service version 2.8.
The full list of changes is given in the official release from OpenStack
7. Update of Keystone to the Rocky version (v.14.2.0)

Date of update: 05 October 2020.
Main changes:
- Implementation of support for the a new hierarchical enforcement model in addition to several improvements to the unified limits of API.
- Parts of the Keystone API have been converted from a user implementation of WSGI to use flask and flask-restful. This may affect people using customisable middleware or introducing customisable insertion pipelines.
- The token provider API has been redesigned to provide cleaner interfaces, which reduces the technical debt. This may affect a deployment using customised token providers.
- Keystone now creates 2 roles by default (member and reader) in addition to the admin role during installation or restart. By default these roles will be included in other service policies in future in order to simplify RBAC in OpenStack. Please note that this may affect deployment due to case-sensitivity problems when naming the roles.
The full list of changes is given in the official release from OpenStack
8. New OS images
Date of update: 13 July 2020.
Main changes:
The list of images available to you for creating instances has been increased to include the following:
- Focal-server-cloudimg-amd64 (Ubuntu Server 20.04 LTS)
- CentOS-8-GenericCloud-8.1.1911
- Debian-10-openstack-amd64
- Kerio-control-appliance-9.2.9
The full list of images available is given in our article OS Images
9. Migration of CEPH storage to Luminos Bluestore completed
Date of update: 15 June 2020.
Work on setting up new software on CEPH storage nodes has been completed, enabling the move to the new BlueStore architecture.
This new architectural solution increases the reliability and stability of systems thank to a reliable mechanism for verifying each data block via a checksum while also changing the IO template during write operations to reduce the likelihood of split-brain.
This work also constitutes the next step towards launching the second Availability Zone, which will enable SIM-Cloud users to deploy high-availability infrastructures by doubling or clustering services.
10. Support for instances with UEFI
Date of update: 29 April 2020.
The option of launching instances that use UEFI has been added. This option will be particularly useful for users who are migrating to SIM-Cloud from other services, where UEFI was used for deploying the virtual machines.
11. New groups of instance types with support for high-frequency processors
Date of update: 26 March 2020
- New servers with high-frequency cores have been added to SIM-Cloud’s pool of computing resources (hypervisors).
- A new group of instance types, ‘Power Flavors’, has been developed with support for high-frequency processors.
New instance types of the ‘Power Flavors’ group have been developed for services and applications that require a higher and more consistent vCPU processing capacity.
The ‘Power Flavors’ have a higher level of performance. These types of instance are based on high-performance Intel® Xeon® Gold 6246 processors with a clock frequency of 3.3 GHz.
It is important to note that 3.3 GHz is the base clock frequency, and that at peak loads the processor frequency could reach 4.2 GHz - this is the maximum clock frequency that can be obtained using Turbo Boost technology.
More information on the new instance flavors is available in our article Instance types (flavors)
12. Update to the backup and recovery service (BaaS)
Date of update: 12 February 2020.
A range of changes and improvements have been prepared in order to optimize the BaaS backup service. These changes have enabled the service to operate faster, more reliably and more transparently for the user. A number of errors and inaccuracies in the operation of the system have been corrected.
In addition, some of the optimisation efforts were directed to preparing BaaS for a forthcoming, more global update that would enable the potential of the service to be discovered and reveal new possibilities for it.
Main changes:
Use of backup plan instead of tasks
The BaaS backup and restore service is entering a new stage of development, as a part of which further improvements and updates are being planned. In the present stage a changeover has been made from using tasks (jobs) to the use of backup plans as a more complex system of actions for creating secured backup copies.
Further, based on the backup plan, our team plans to implement more flexible and functional packages for creating backups that will contain not only disk data but that can optionally also save backup data according to additional disk or instance parameters and also their configurations. This step will allow users to be offered an updated service with new possibilities that guarantee stability and reliability.
Simplified procedure for disabling backup for a disk
Optimisation has been completed of the disabling procedure for disk backups, now added to the BaaS backup plan. To disable a disk for BaaS it is now necessary to: 1) Go to the Backups section. 2) Select the disk (by name) to be disabled for backup, and in the
‘Actions’ column then select ‘Disconnect disk’. Once the ‘Disconnect Disk’ button is pressed, the process begins of disconnecting the service snapshot used for backing up. This process may take a short time. The disconnected disk is also removed from the backup plan.
- Once the disk has been disconnected from the backup service, you can remove the disk from the ‘Disks’ section.
- If the backup plan contained only one disk, which was disconnected from backing up, this task should be disabled or deleted, as launching it may result in an error.
- The disconnected disk cannot be added to a backup plan if backups for this disk already exist. To reconnect the disk to BaaS, first delete the old backups for the disk.
Improvements have been made to the monitoring process for BaaS
Our engineers have completed a series of improvements to the monitoring of the backup service, which should enable even greater reliability and availability. New metrics will help in effectively tracking changes in the functioning of the service.Changes have been made to the display of execution time of backup plan tasks
Now the processing time of tasks (launch and completion) is displayed in the user’s time zone, which is set in the cloud dashboard (https://cloud.sim-cloud.net/settings/). The time of processing of tasks will be displayed in the correct time in these sections: - ‘Overview’ - ‘Tasks running’ and ‘Backup plans’ - ‘Tasks running’. It should be noted that the user’s time setting is stored only in the cookies of your web browser. The backup service stores all time settings in the UTC (Coordinated Universal Time) standard. This means that when configuring the schedule for the tasks in your backup plan, the times must be specified in UTC.Optimisation of processing and display of elements of BaaS
Thanks to changes made in the processing of elements of the backup service, the speed of display of restore points in projects with a large number of disks and backups has been increased.Service tasks are no longer displayed in BaaS settings
The list of backup plans no longer displays service tasks (disconnecting disks, restoring disks). As previously, service tasks can be traced in the ‘Task history’ section.
Project information now added to messages from the BaaS notification service
Messages from the BaaS notification service now contain information on the project name. This will add informational value for users that have multiple SIM-Cloud projects activated; they will now see at a glance to which project the e-mail notification relates. The format of the notification will be as follows:
- Date and Time
- Backup plan “< backup_plan_name >” <operation>
- Project: <project_name> (<project_id>)
The process of deleting restore points in backups has been optimised
Changes have been made to the algorithm for processing backup deletion tasks. This optimisation has made the process more reliable and more efficient and shortened the time required for deleting restore points, as well as eliminating small errors when removing disks for which a backup plan had been configured.The display of efficiency diagrams for use of BaaS has been corrected
Changes have been made to the display of efficiency of use of BaaS: now the calculation of the coefficient of use efficiency of the backup is performed more accurately.
Correction of error when creating backups for disks with zero volume
Corrections have been made to the algorithm for creating restore points for disks with zero volume. Disks that do not contain information and also do not have partitions can now be successfully added and processed in BaaS backup plans.
13. Introduction of 3-factor replication for Ceph storage
Date of update: 25 January 2020.
The changes affected the configuration of Ceph storage, which is used to provide CS1, Tier IV (SATA) storage capacity. All storage areas indicated above in the avz1 availability zone have been converted to factor 3 replication.
The replication factor is the level of redundancy of data in storage. The number of copies of the data that will be stored at various nodes and on various disks has been increased by a factor of three. This means that every object in the storage is stored in triplicate, and moreover, each copy is stored on a different node. This change will significantly increase the reliability of data storage in our storage volumes and increase its availability and persistence.
14. New type of S3 storage
Date of update: 22 January 2020.Available from early 2020, secure object storage based on the S3 protocol is an ideal solution for storing a variety of file and media archives, for working with big data and also for web development and storage of static content.
A flexible, practically dimensionless universal storage that is compatible with S3. With a high level of security and fast data transfer.
You can find out more about the new cloud service in our article: S3-compatible storage.
15. Change of name of general storage type
Date of update: 03 September 2019.
Main changes:
- The name of the general storage type for the volumes of instances was changed in SIM-Cloud projects from ‘Tier II (SSD)’ to ‘gs1’.
The fundamental technical characteristics of GS1 storage have not changed: * Bandwidth: 300MB/s * IOPS: 10000/s.
Two types of storage are available to SIM-Cloud users, both based on Ceph:
- gs1 is general storage, universal storage; it is used for most services, it is also suitable for data-intensive applications with high levels of data exchange.
- cs1 is a type of storage intended for low-load tasks.
16. New instance types (‘flavors’)
Date of update: 27 June 2019.
Main changes:
New types of instances have been developed and introduced that cover most requirements for deployment of modern systems and services, including data-intensive applications.
All available templates satisfy the requirements of NUMA topology for the utilisation of the processing possibilities of hypervisors, which provides the maximum efficiency of computational resources to the user.
More information on the new instance flavors is available in our article Instance types (flavors)
17. Addition to the SIM-Cloud web interface of option to use notifications about events in BaaS
Date of update: 26 June 2019.
Main changes:
- Now it is possible, via the cloud management interface (dashboard)
https://cloud.sim-cloud.net/project/duratus_notifications/ to configure the sending of notifications to e-mail addresses by different events in BaaS.
18. New type of CS1 storage
Date of update: 21 June 2019
Main changes:
- New storage type ‘CS1’ (Cold Storage) created. The new storage is available to users of SIM-Cloud projects for creating instance store volumes.
- The new CS1 storage has the following technical characteristics:
- Bandwidth: 200MB/s
- IOPS: 750/s.
- CS1 storage was created to replace Tier IV (SATA). Bandwidth: 200MB/s IOPS: 500/s. It can be seen that the number of input/output operations (IOPS) is 50% greater for the new storage type, which makes it more functional and desirable for lower-intensity systems and services.
- In addition to its improved performance, available thanks to optimisation and correction of the architectural solution of the Ceph cluster, the stability and fault tolerance of the storage has also been increased.
19. Update of Keystone to the Queens version (v.13.0.2)
Date of update: 20 June 2019
Main changes:
- In this release, support is added for application credentials: a new method of verifying the authenticity of applications using Keystone. Rather than storing the user name and password in an application configuration file (which may pose a threat to security), it is now possible to create login credentials for the application, such that the application itself undergoes the authentication check and receives the scope and role previously allocated to it.
- Deletion of support for all API Identity v2, with the exception of API EC2 v2, from Keystone
- When working with LDAP, all users and groups must have a name. Previously, Keystone allowed LDAP users and groups to simply use space characters instead of a name.
- Since Keystone is not a policy manager, ‘policies API’ has been declared obsolete and is not used.
- LDAP attribute names are now used without case sensitivity.
- Correction of errors and increased operational stability.
The full list of changes is given in the official release from OpenStack
20. Update of Nova to the Queens version (v.17.0.9)
Date of update: 18 June 2019Main changes:
- Cells v1 and nova-network declared obsolete.
- The drivers libvirt and xenapi compute now have an (experimental) native support for virtual graphical devices.
- The compute driver libvirt now supports volume multi-attach support when using API version 2.60. Connection of the volume to several instances is possible in NOVA only when the volume was created in Cinder with the flag multiattach=True. Responsibility here for the data integrity is with the user by setting read/write regimes for this volume on different instances. Currently this function is supported only by the compute driver libvirt, and only when qemu < version 2.10 or libvirt> version 3.10 are installed on the compute host.
- If QEMU version 2.6.0 or higher, Libvirt version 2.2.0 or higher and the ‘luks’ volume encryption provider are installed, then decryption of RAW files, block and network devices (such as rbd) can be done directly using QEMU.
- Nova no longer supports API v2 for block storage (Cinder). The current version is API v3.
- The following nova-manage commands have been deleted: quota, shell, project, account, logs, host, agent
The full list of changes is given in the official release from OpenStack
21. Update of Neutron to the Queens version (v.12.0.5)
Date of update: 19 May 2019
Main changes:
- Support for the VPNaaS service is now implemented as an extension of the L3 agent.
- The DHCP refresh timer parameter (T1) can now be changed manually. The benefit of changing the value of T1 is that if the DHCP server becomes unavailable at the end of the lease term, the instances will not discard their IP addresses.
- It is now possible to specify to the DHCP agent not to assign just any DNS server address to its clients by setting the attribute ‘DNS Name Servers’ for the relevant subnet to ‘0.0.0.0’ (for IPv4 subnets) or ‘::’ (for IPv6 subnets). In the old behaviour, each DHCP agent offered its clients only its own IP address as a DNS server. The new behaviour, however, is that the DHCP will no longer offer any DNS server IP address.
- The time spent processing security group updates in agent L2 has been reduced and the contraction removal is now performed in a set of work streams instead of the agent’s main stream, and therefore this can return quickly to processing other events.
- Implementation of floating IP QoS. The new parameter qos_policy_id has been added to the API linked to the floating IP.
The full list of changes is given in the official release from OpenStac
22. Update of operating system images
Date of update: 17 April 2019
Main changes:
- The list of available OS images has been updated; you can see the entire list of changes on our website
- Images of operating systems include all the latest updates.
23. Update of Cinder to the Queens version (v.12.0.4)
Date of update: 22 March 2019
Main changes:
- API support for versions 1.х withdrawn The current version is API v3.xx.
- Starting from Cinder version 12.0.0, the ‘policies in code’ principle applies. This means that the code specifies reasonable default values that can be overridden (this requires that a policy file be created with the parameters of the override).
The full list of changes is given in the official release from OpenStack
24. Update of Glance to the Queens version (v.16.0.1)
Date of update: 12 March 2019
Main changes:
- A new method of loading images has been added: ‘web-download’. This allows an image to be copied from a remote URL to a local image storage.
- API support for versions 1.х withdrawn. The current version is API v.2.6.
- The possibility was added of adding metadata to images ‘on the fly’ during the importing process.
The full list of changes is given in the official release from OpenStack