Quick start¶
- Accessing the SIM-Cloud dashboard
- Project resources overview
- Creating the disk
- Launching the instance
- Assigning a floating IP
- Changing security groups
- Exiting the SIM-Cloud dashboard
In this section we examine several aspects that will assist you in adapting to the SIM-Cloud service interface and with the most important factor: getting started quickly with running your infrastructure in our cloud.
- Overview of project resources after activation.
- Quick deployment of an instance, plus the settings for remote access to it.
- Creating a disk and launching the instance under the MS Windows 2016 Standard operating system.
- Assigning a floating IP address for the instance and basic settings for remote access by RDP.
- Accessing the SIM-Cloud dashboard
1.1 Open the web browser, with JavaScript and cookies enabled.
Note
We recommend that you use the latest version of either Google Chrome or Mozilla Firefox.
1.2. In the address line of the browser, enter the URL: https://cloud.sim-cloud.net/.

1.3. On the login page that appears, enter your username and password, then press ‘Connect’.
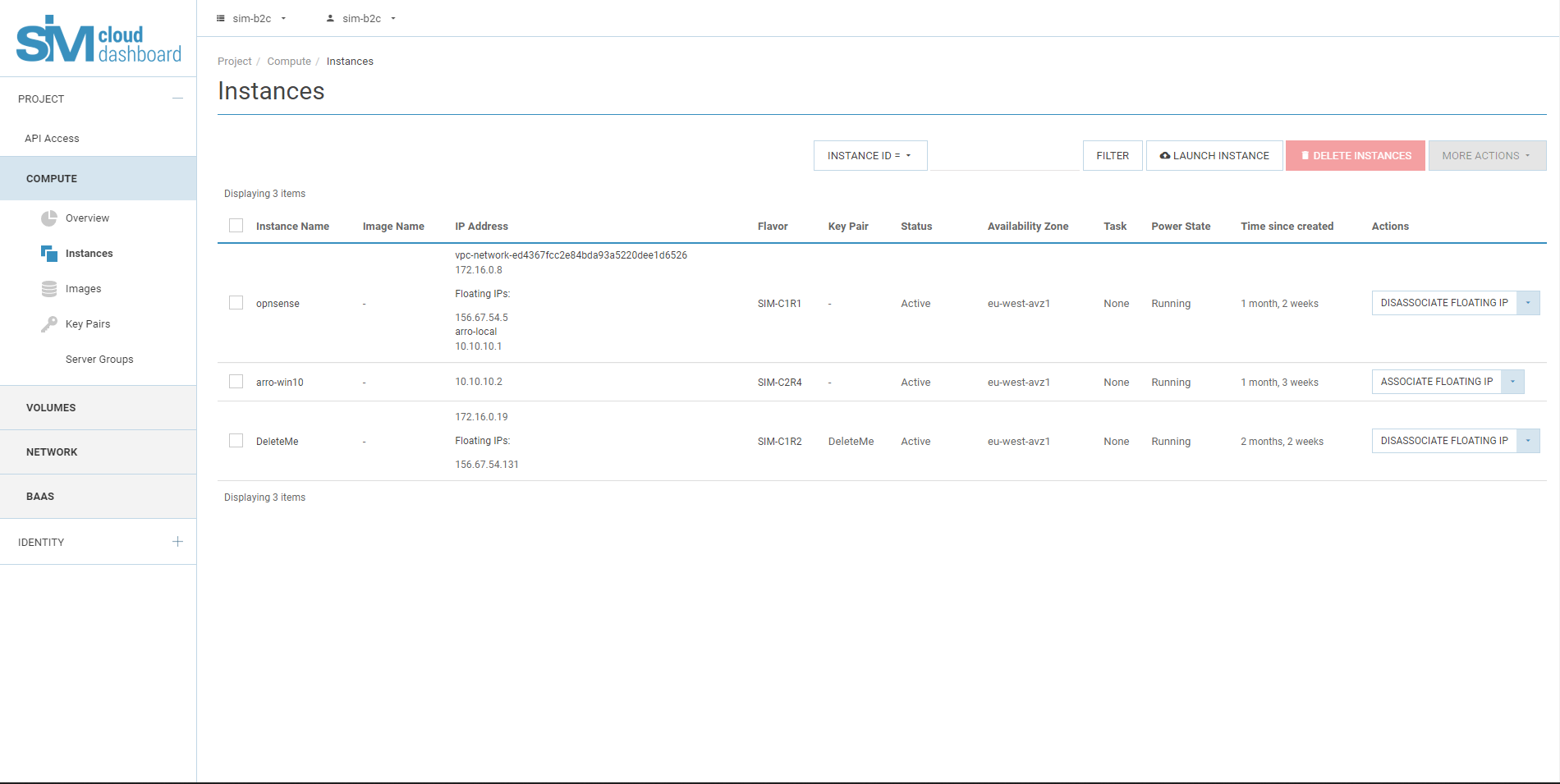
- Project resources overview
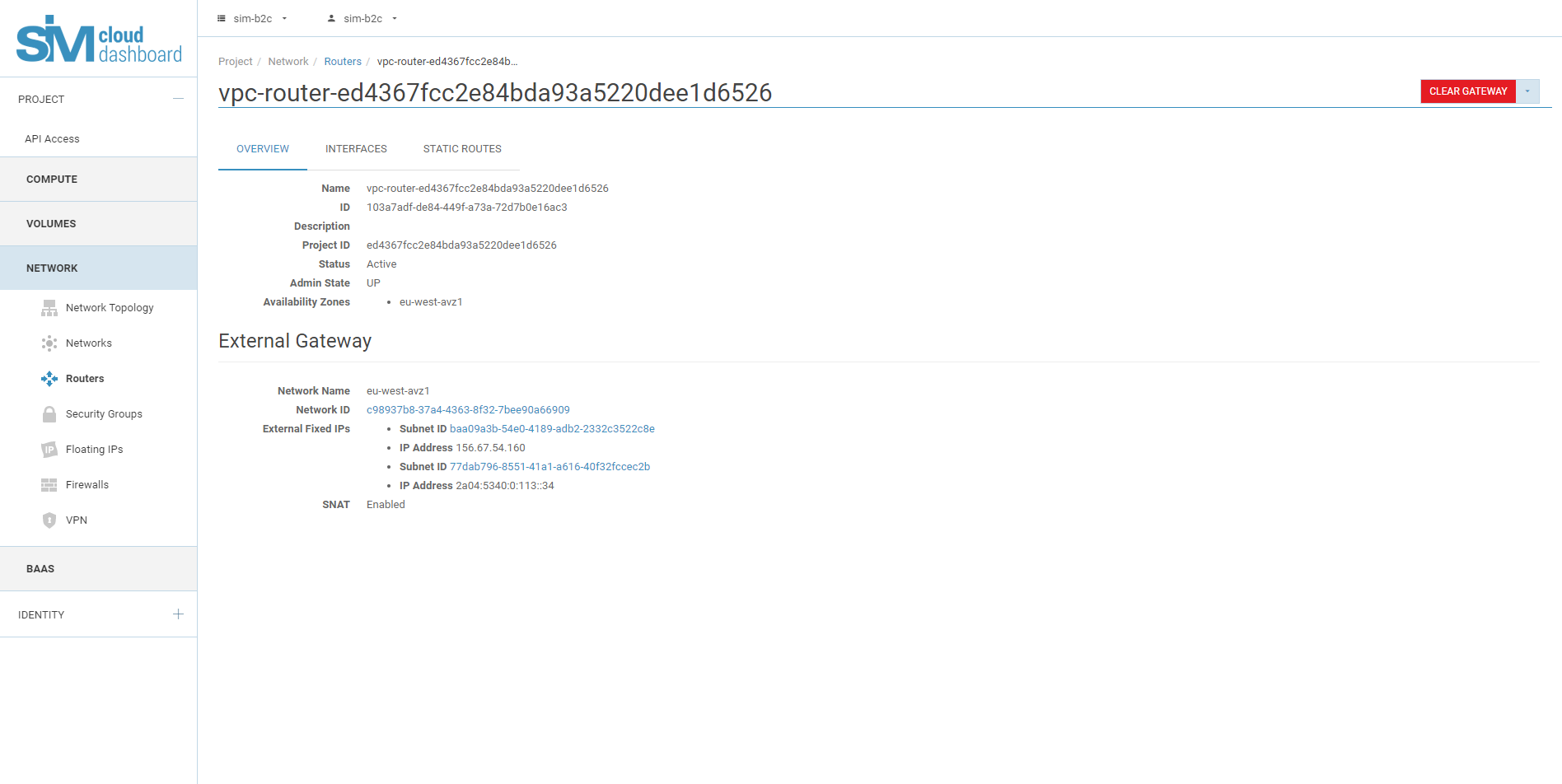
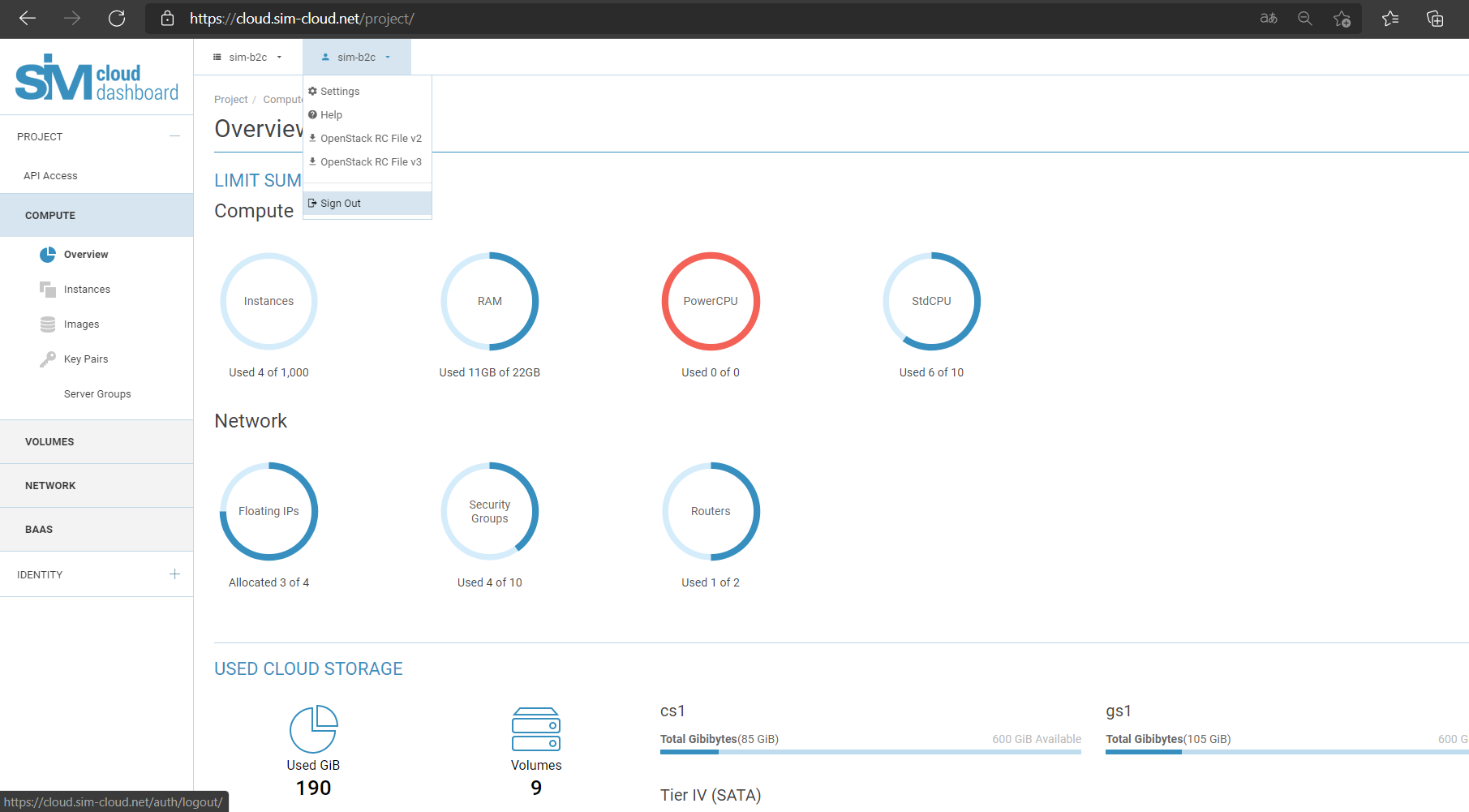
Every SIM-Cloud project is created with a defined set of computational resources. The quota for all computational resources is assigned at the point of activation. The available free resources of the project allow you to create infrastructure objects such as instances, disks, routers, networks, subnetworks, backup copies, VPN services and so on. Before deploying your infrastructure you should check your quota of available resources.
Before deploying your infrastructure you should check your quota of available resources.
- Computational resources (vCPU, RAM, storage)
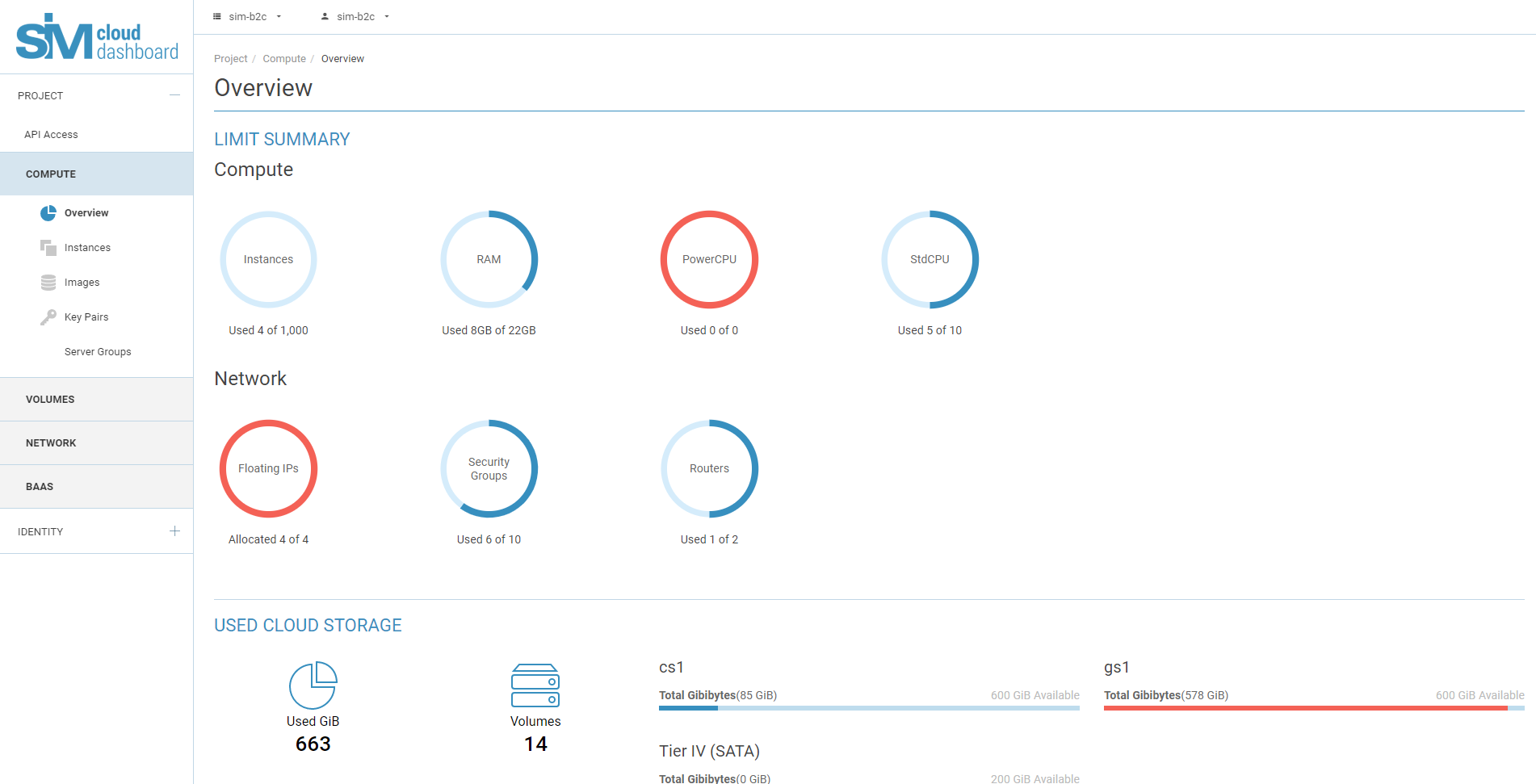
- Network resources (routers, subnetworks, floating IPs)
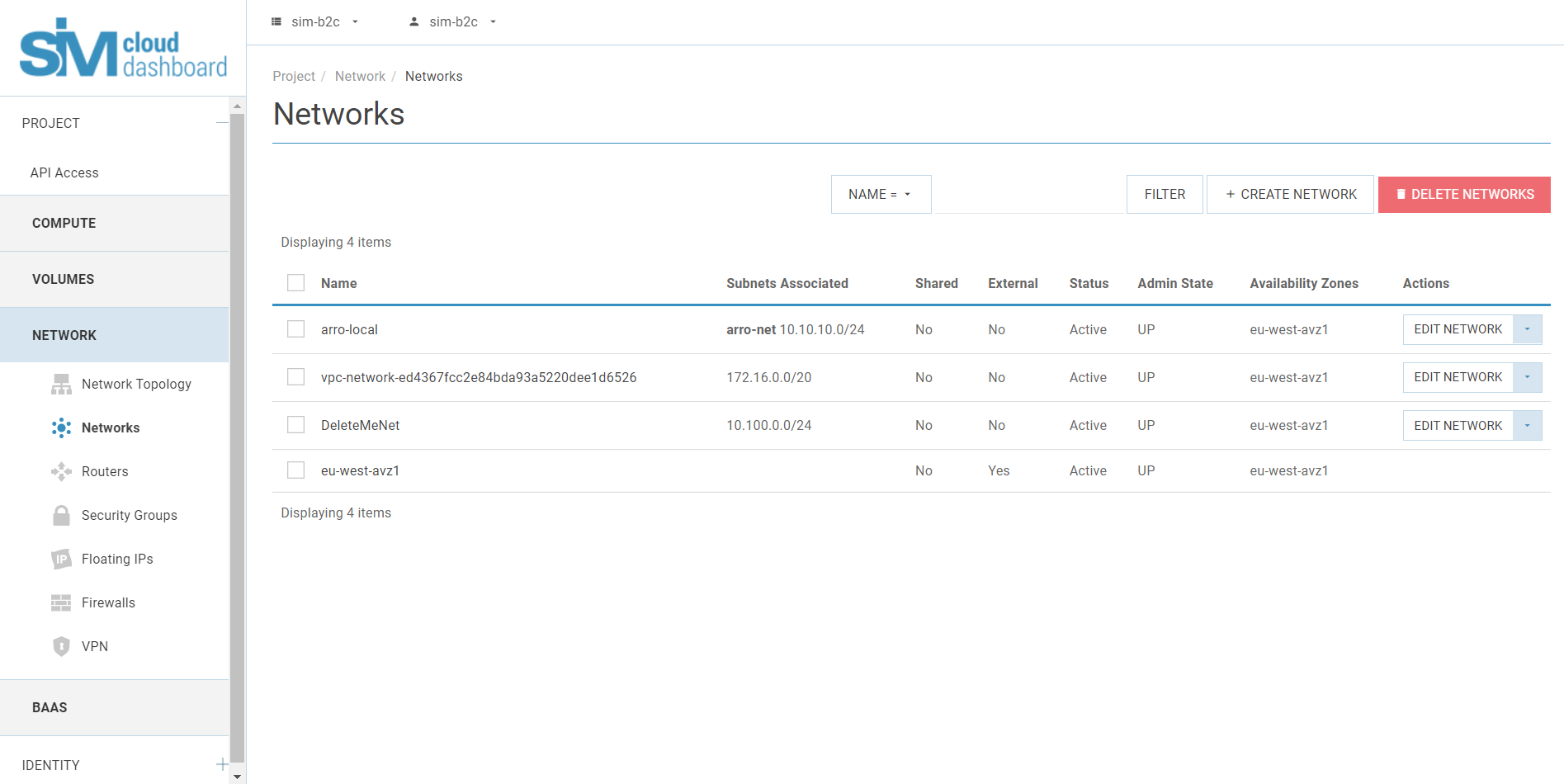
By default, SIM-Cloud projects are activated using already created network objects:
- One router (with the name vpc-router-project id);
- One network (with the name vpc-network- project id and one subnetwork 172.0.0.0/8), with DHCP service;
- One IPv4 floating IP address.
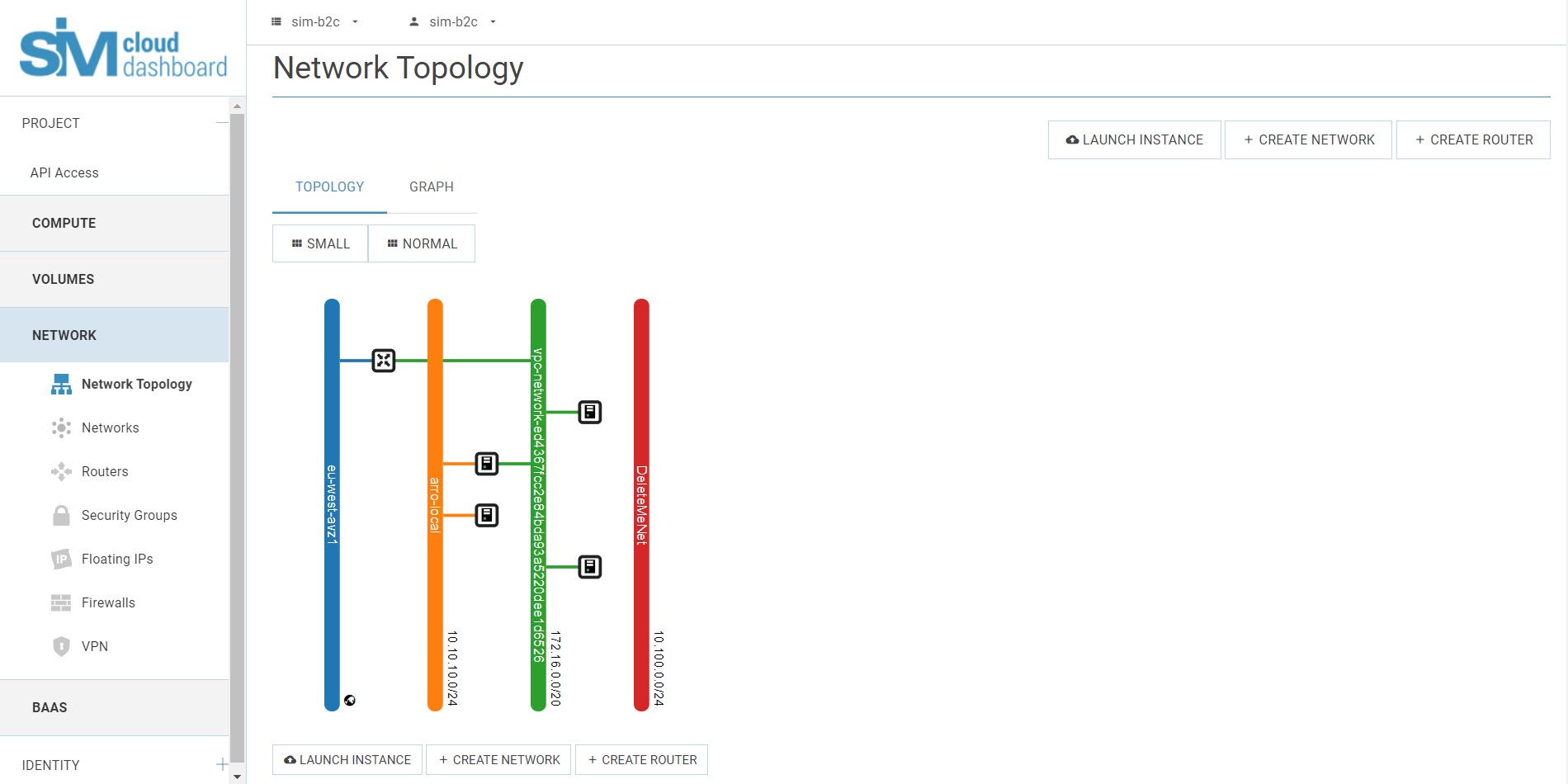
Network elements that have been created in advance enable the required infrastructure to be deployed quickly and access provided to the publicly accessible network.
- Creating the disk
The first requirement for launching an instance is to create a disk.
3.1. In the Project tab, open the Disks tab and select the Disks category.
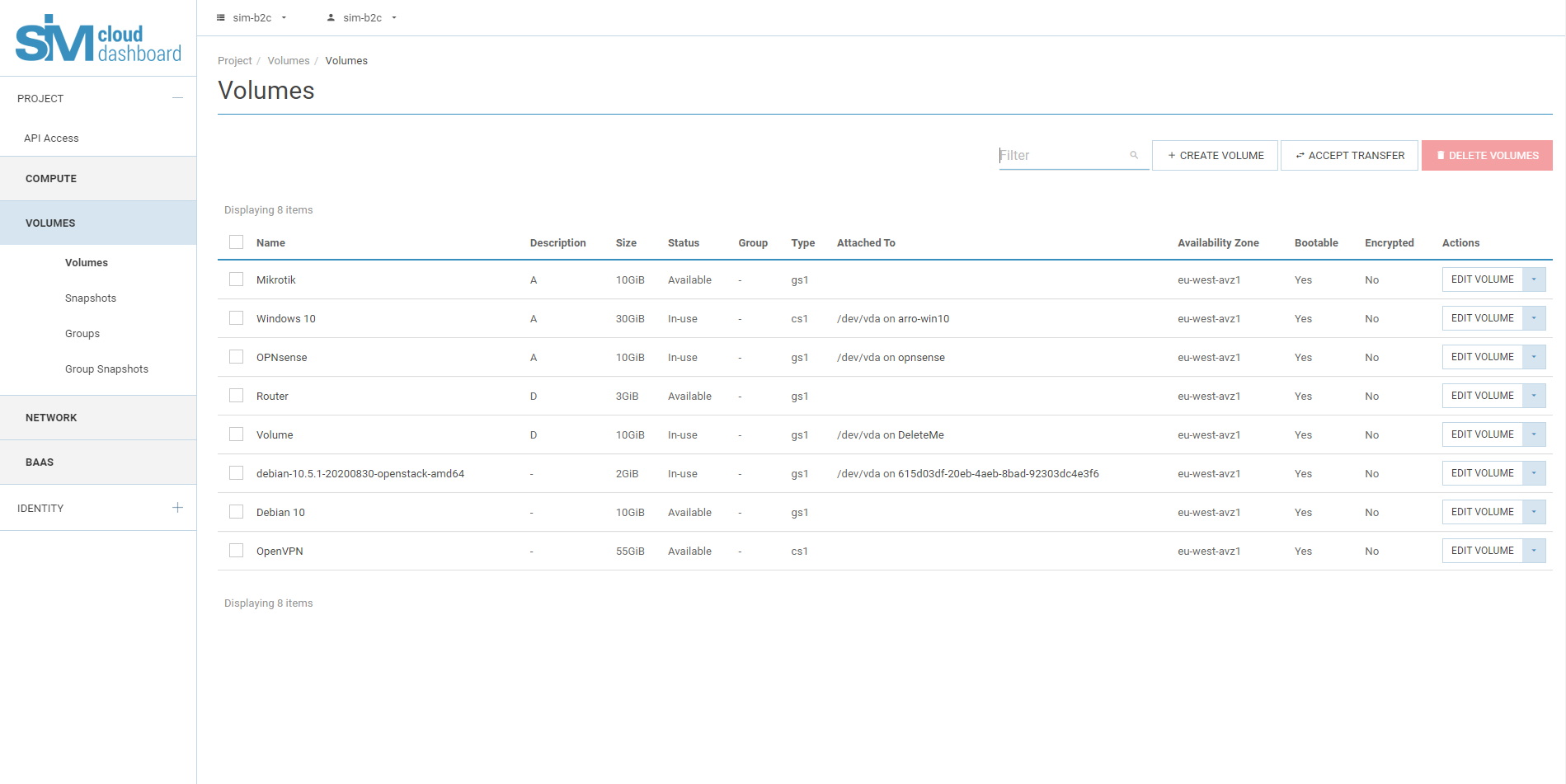
3.2. Click ‘Create disk’.
In the dialog that opens, enter or choose the following values:
If you choose this parameter to create a disk, a new field will appear allowing the use of the image as a source. Select the required image from the list shown. If you create a new system boot disk, you must select an image with the required operating system. If you select ‘No sources, blank disk’, the service will create a blank disk without either a file system or a partition table. You should choose this option only if it is necessary to create an additional disk that can be connected to the instance. In our case we select to create a disk with the image for MS Windows 2016 Standard [RU] Build 14393.
Note
Note that the list of available images for disk creation includes images supported by the ‘cloud-init’ function and also with the included option ‘key-based authentication’. The use of such images will enable the deployment of instances to be accelerated thanks to advance configuration with the aid of the cloud-init scripts, and the use of authentication keys will improve the security of working with the instance. These images include the tags [cloud-init, OS] in their properties. When creating an instance on the basis of images of this type it is essential to specify a key pair for subsequent authentication; if a key is not specified, it will not be possible to complete authentication by password (in which case it will be necessary to recreate the disk using a standard image or assigning a key during a repeated creation; there also remains the alternative option of resetting the passworde using standard Linux OS methods).
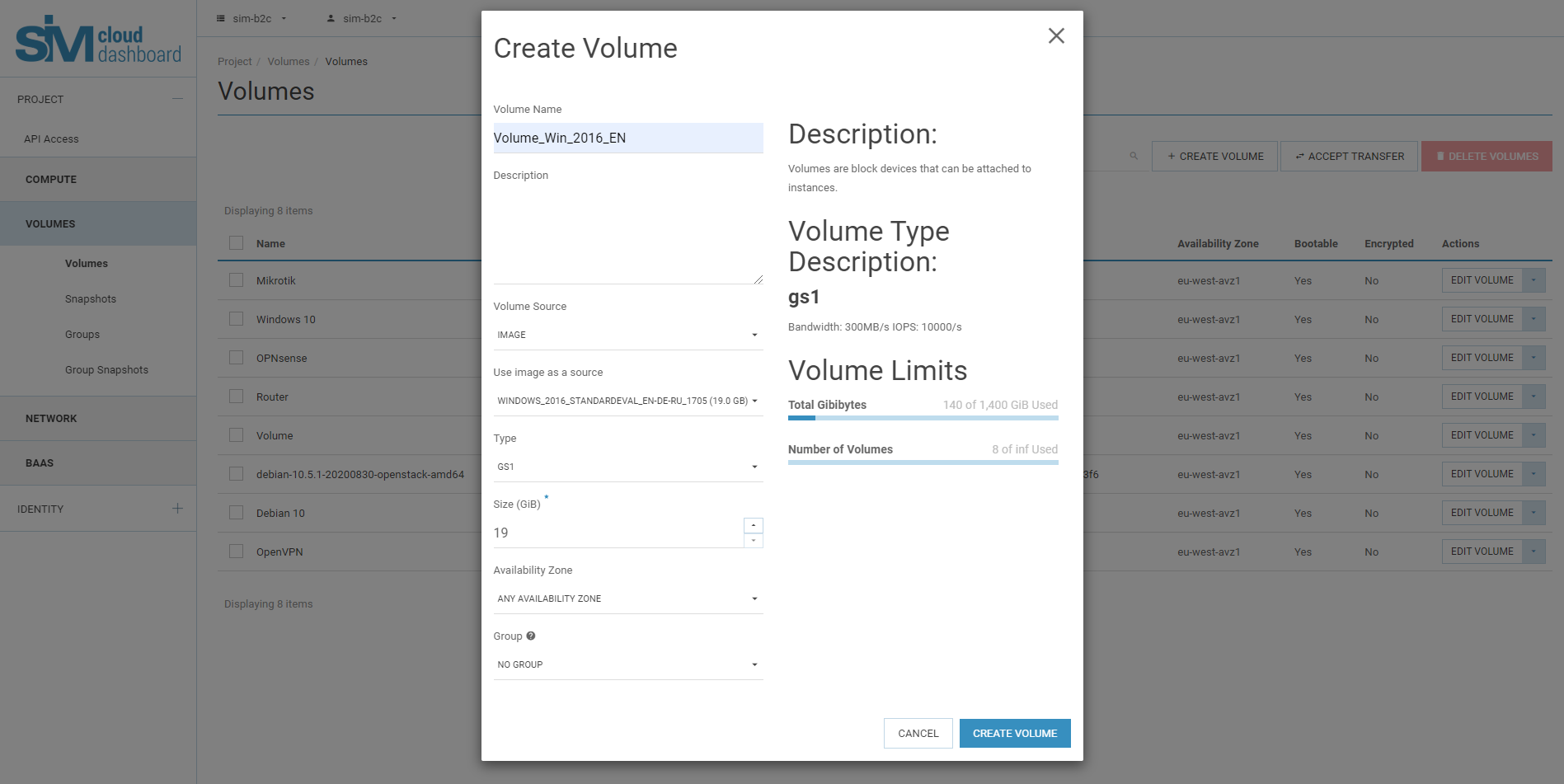
3.3. Click create disc.
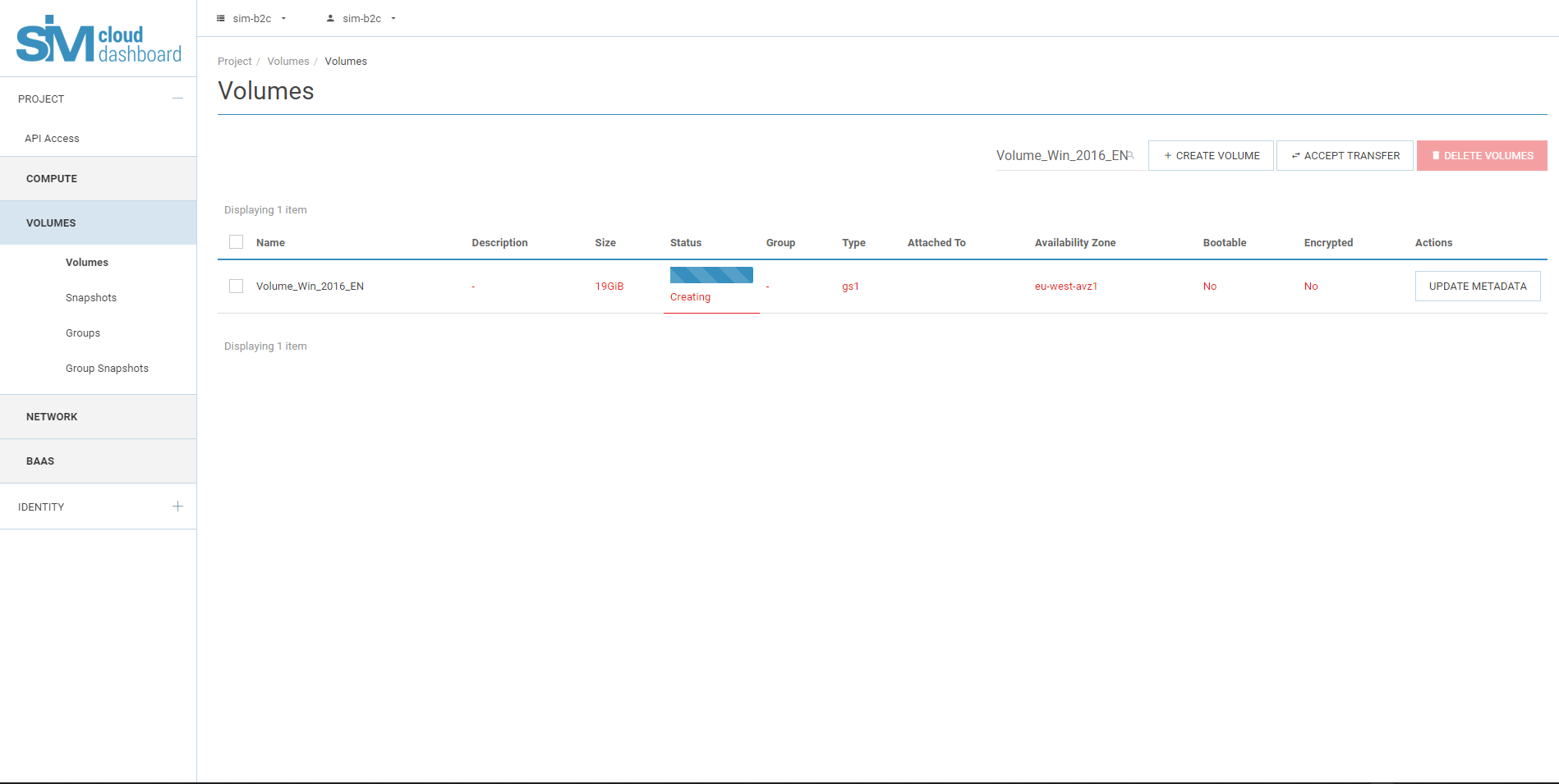
3.4. Disc creation can be seen in the toolbar, in the discs tab.
It may take about 10 minutes for the disc to be created.
- Launching the instance
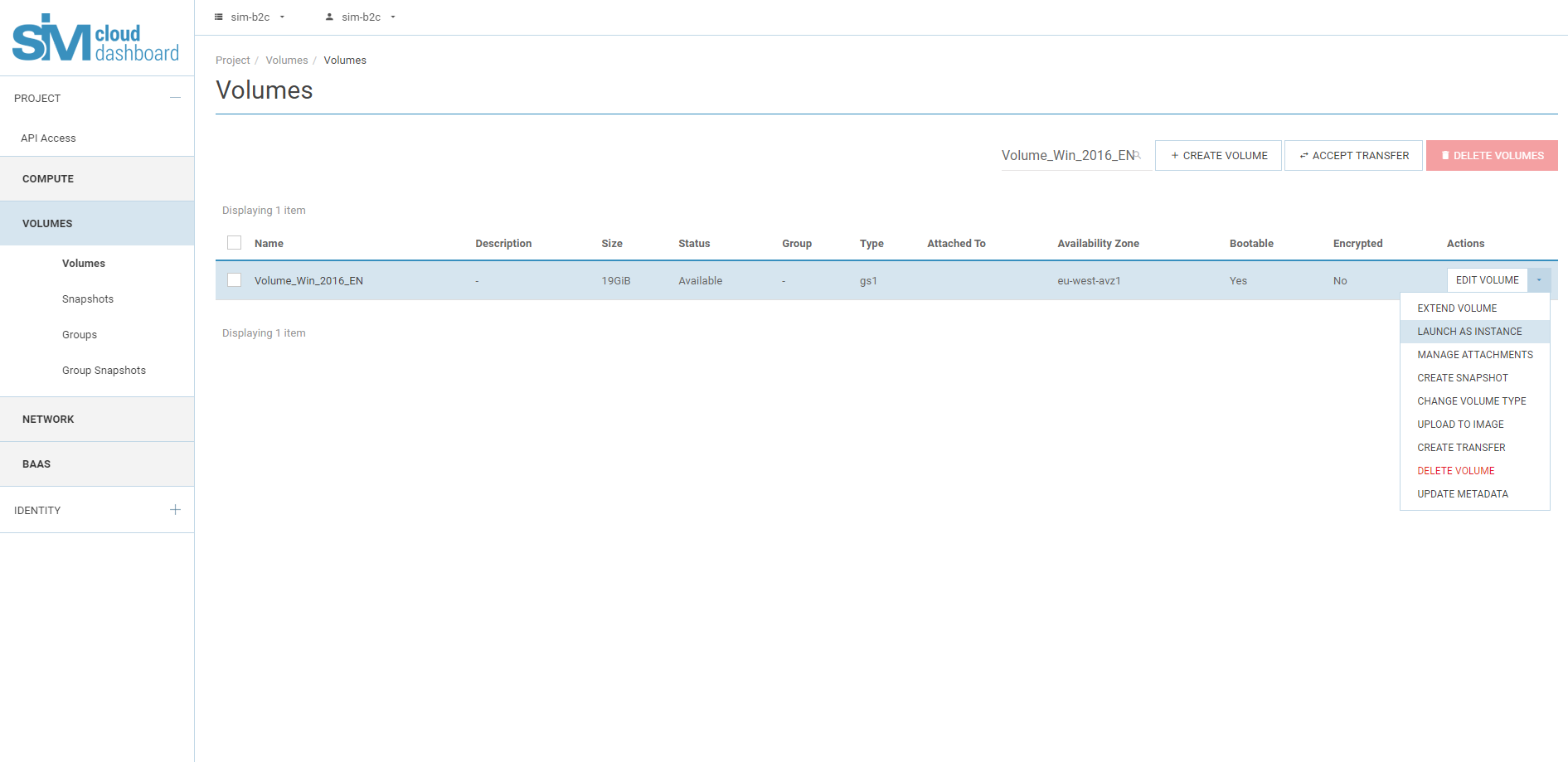
4.1. In the "Project" tab, open the "Computing Resources" tab and click on the "Disks" category.
4.2. The toolbar displays disks with their own attributes: "Name", "Description", "Size", "Status", "Type", "Connected to",
Availability Zone, Bootable, Encrypted, Action.
In the "Actions" column, select the drop-down list for your disk and click "Run as Instance".
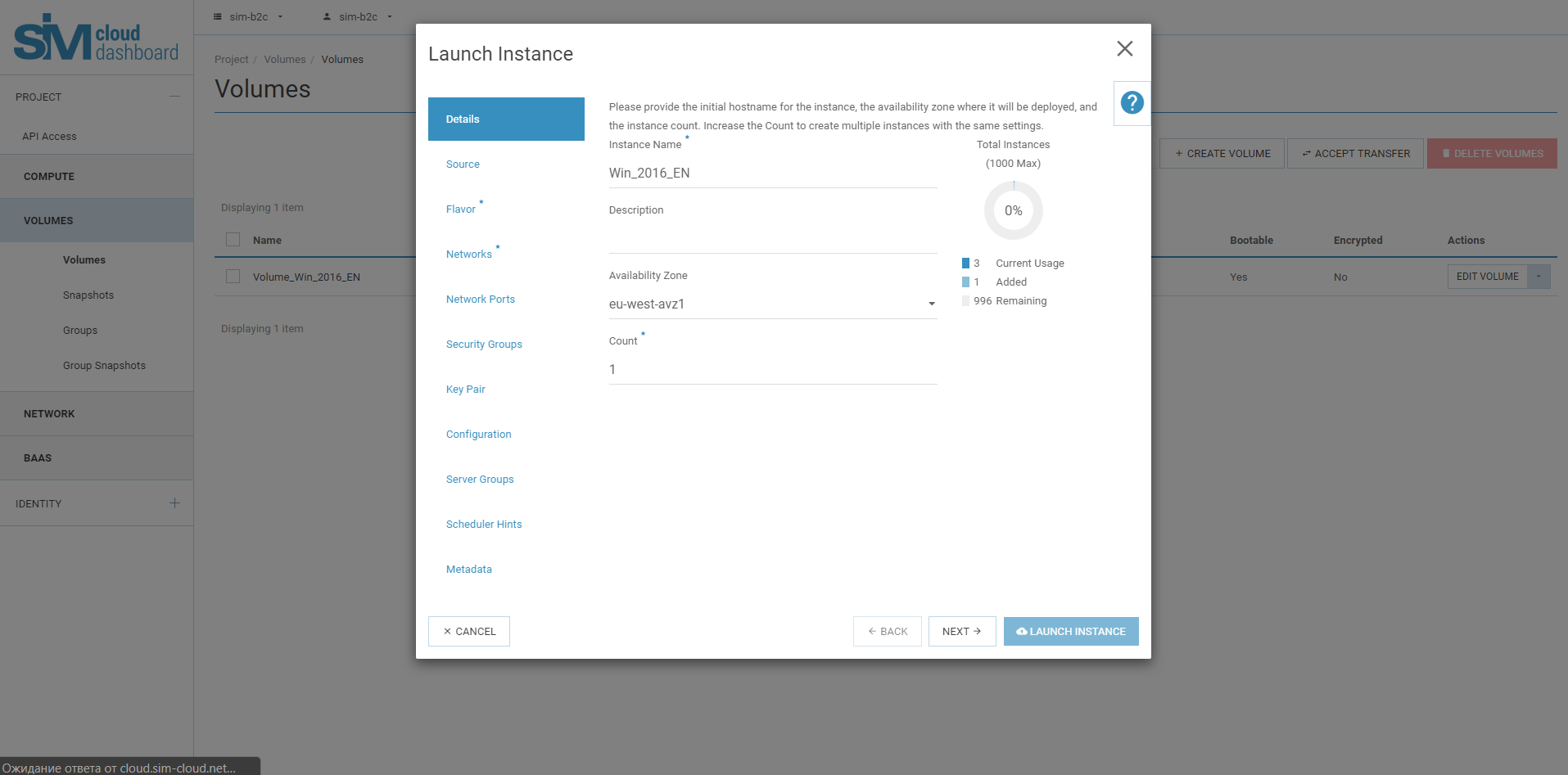
4.3. In the Launch Instance dialog box, specify the following required values.
Details:
Warning
The name you assign here becomes the initial hostname of the server. If the name is longer than 63 characters, the service will automatically truncate it to ensure that dnsmasq works correctly. If, after building the server, you change the server name in the API, or change the hostname directly, the names will not be updated in the control panel. Server names are not guaranteed to be unique when created, so you may have two instances with the same hostname.
In instance naming, it is unacceptable to use Cyrillic and Umlaut (Ää, Öö and Üü), the use of these symbols will lead to an instance creation error.
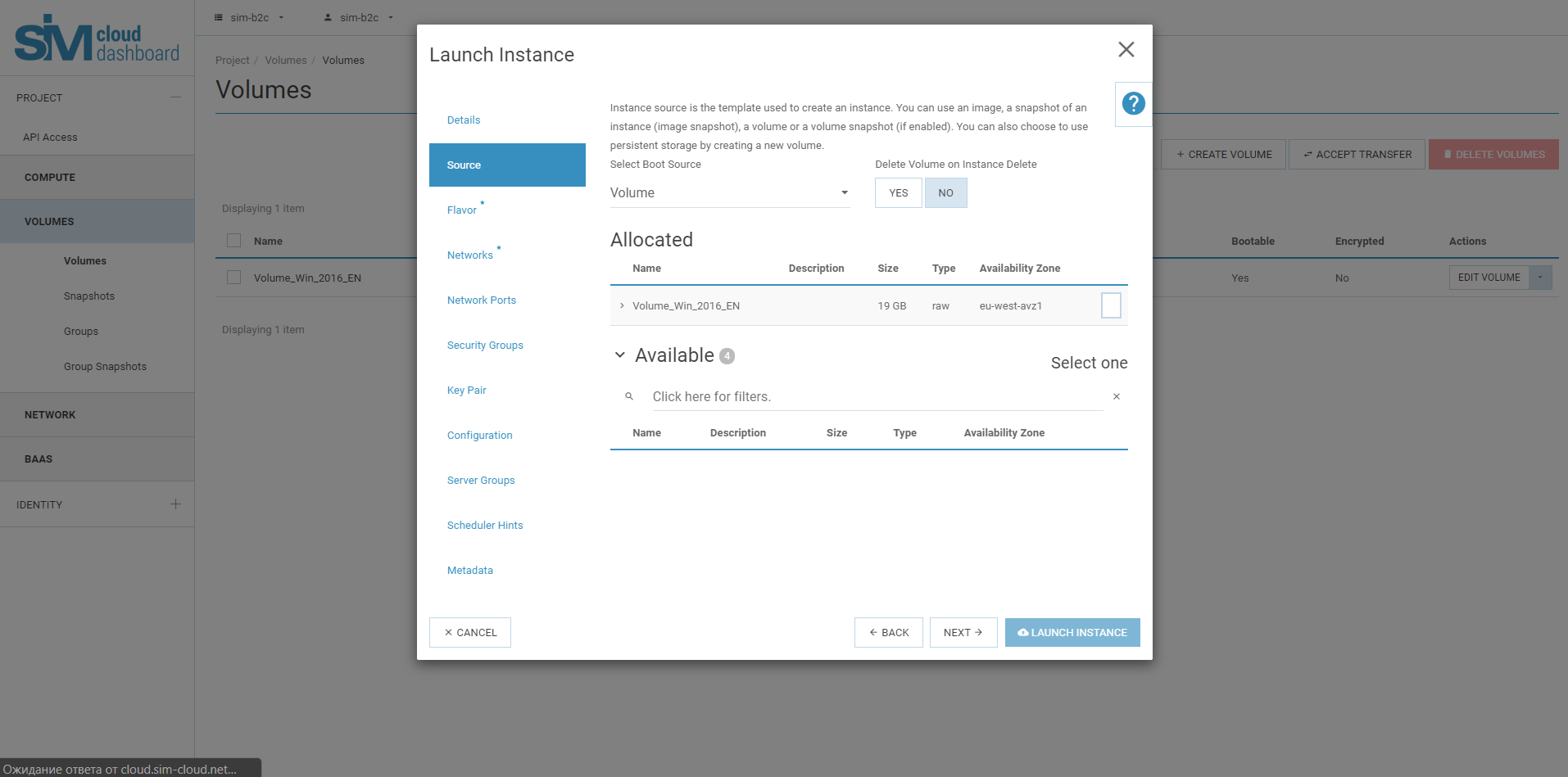
A source:
Instance type:
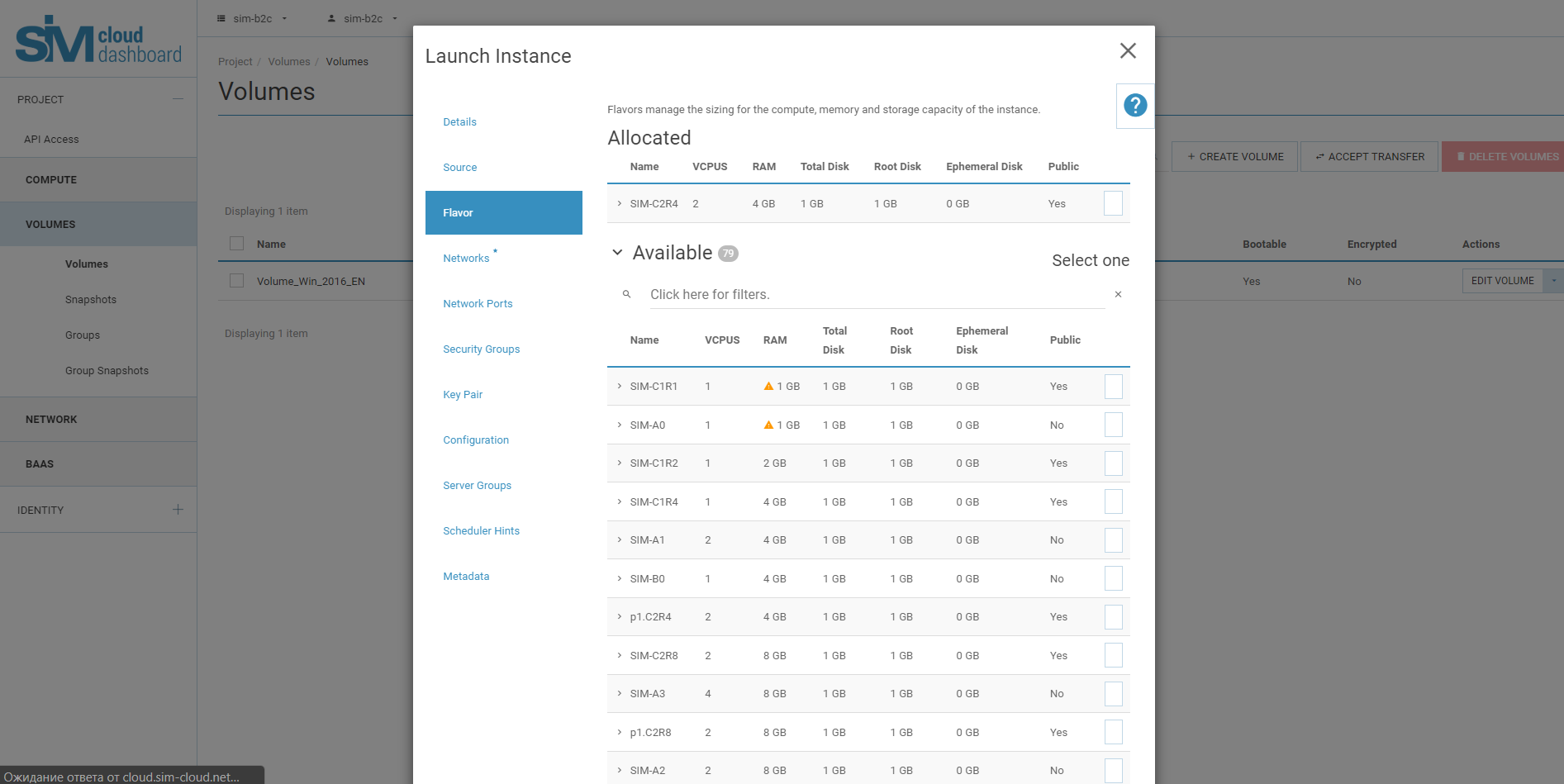
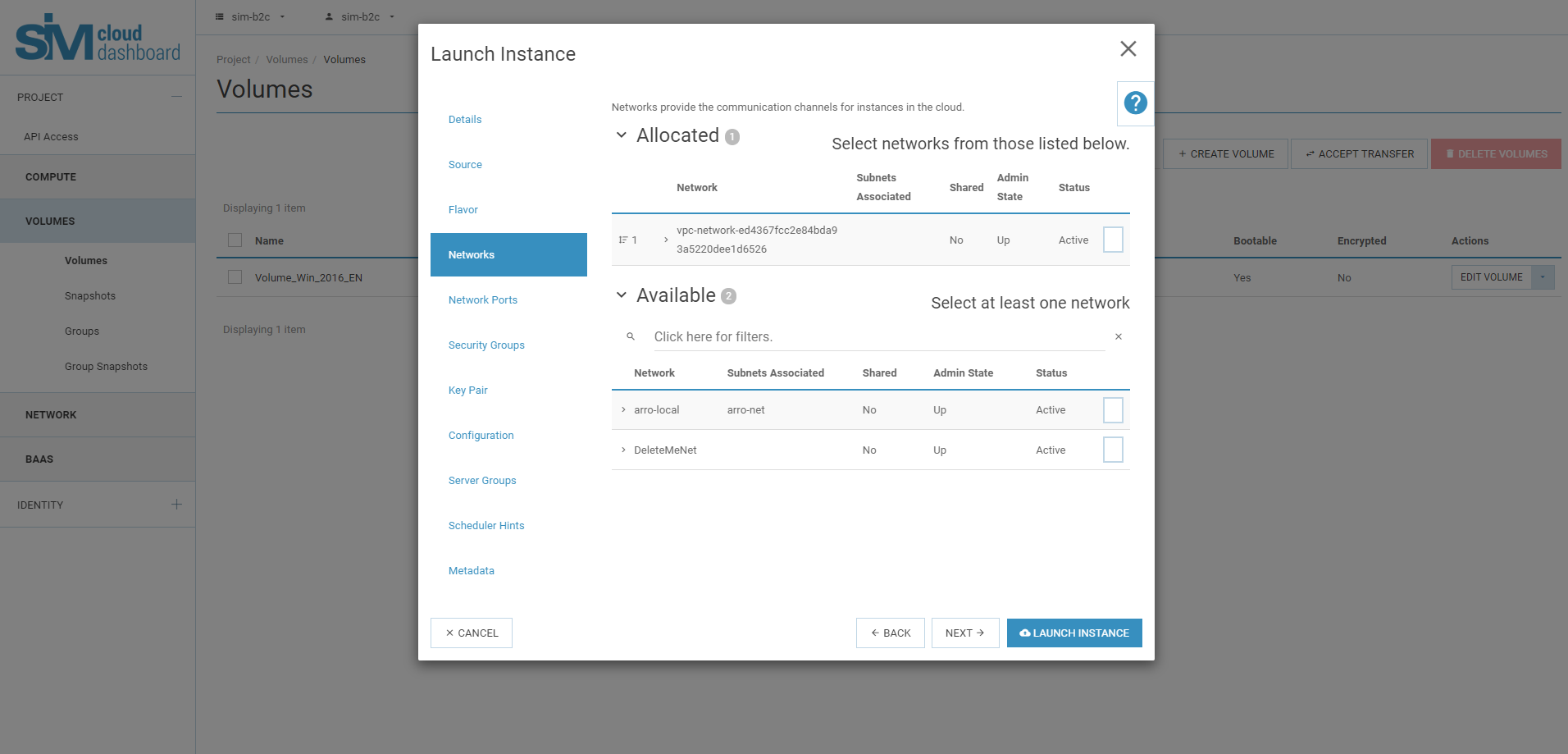
Networks:
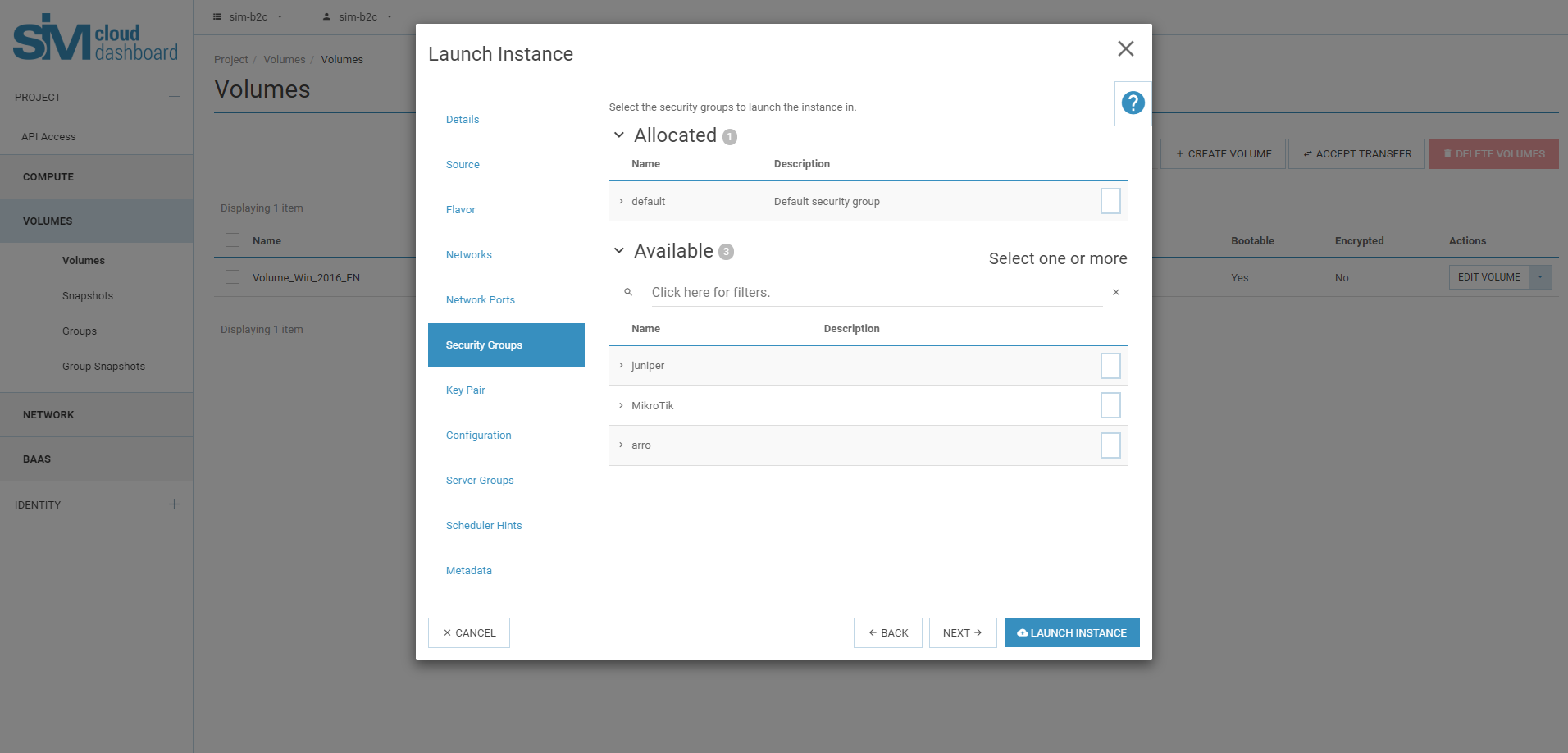
Security groups
Select the security groups that you want to assign to the instance.
- Security groups - it’s kind of
- cloud firewall that determines which network outbound and inbound traffic is redirected to the port of the instance.
If you have not created any security groups, you can only assign the default security group to the instance.
4.4. Click Launch Instance.
The instance runs on a compute node in the cloud.
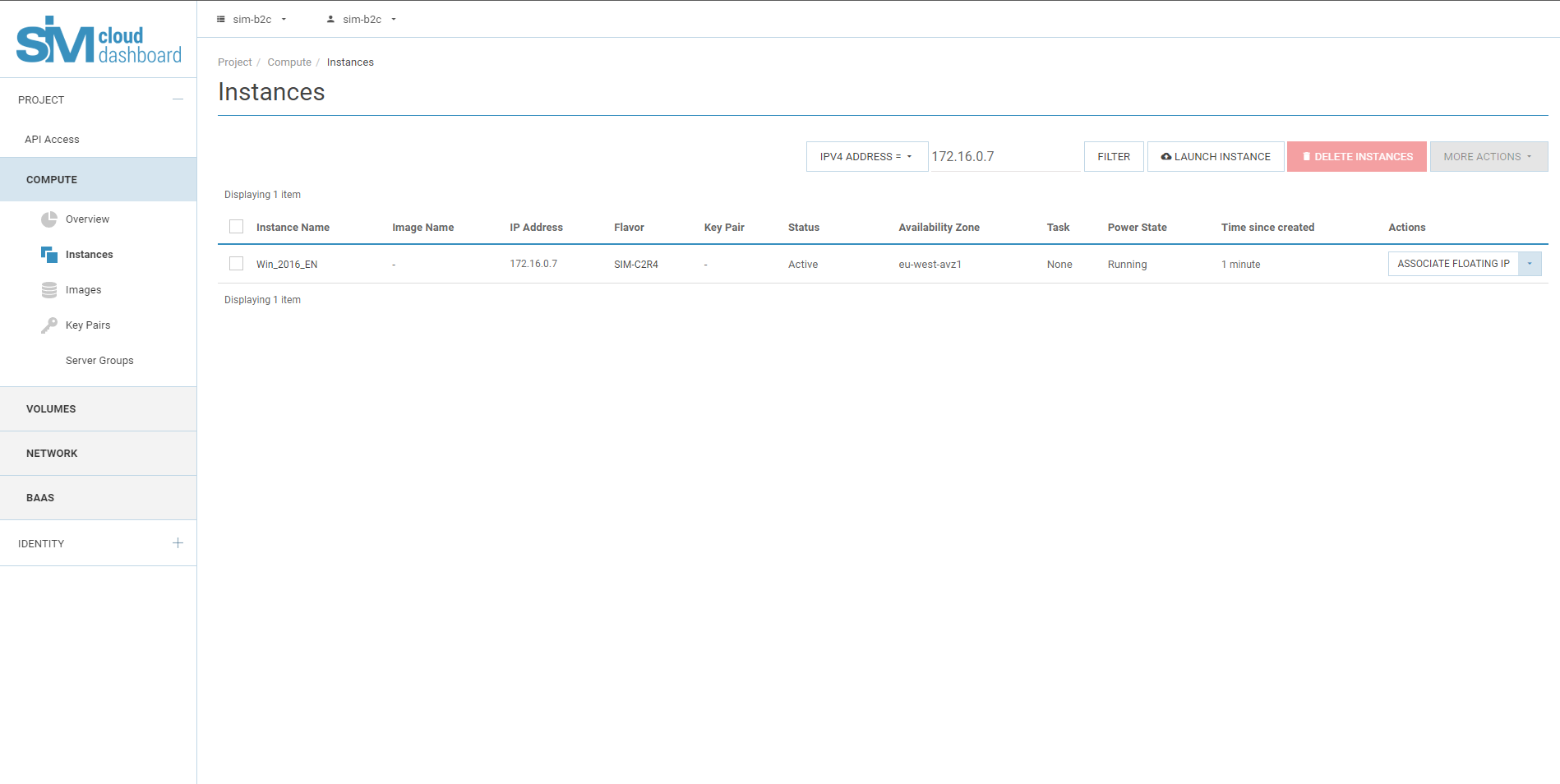
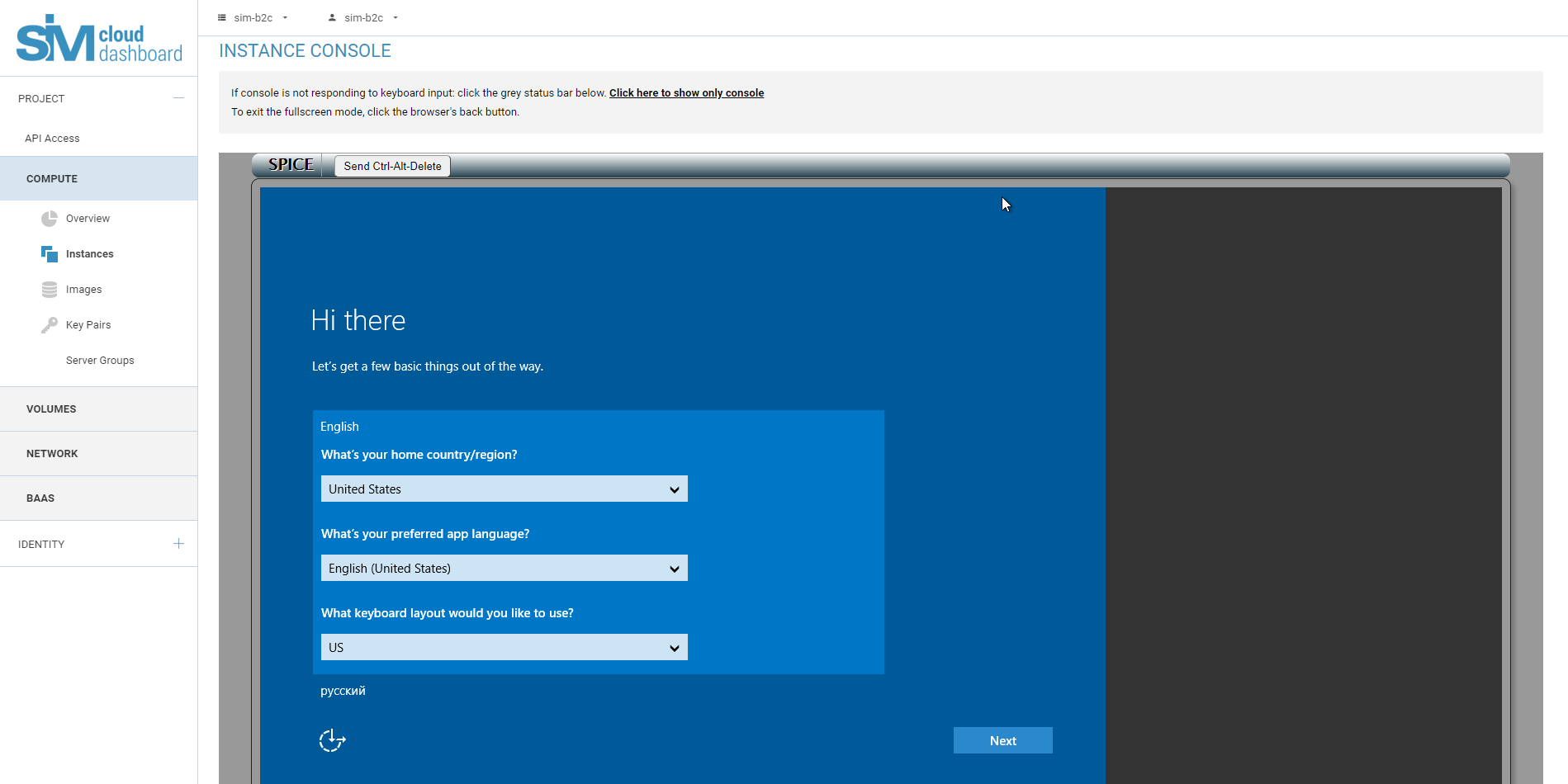
4.5. Completion of the OS installation process.
Access to the instance via the console:
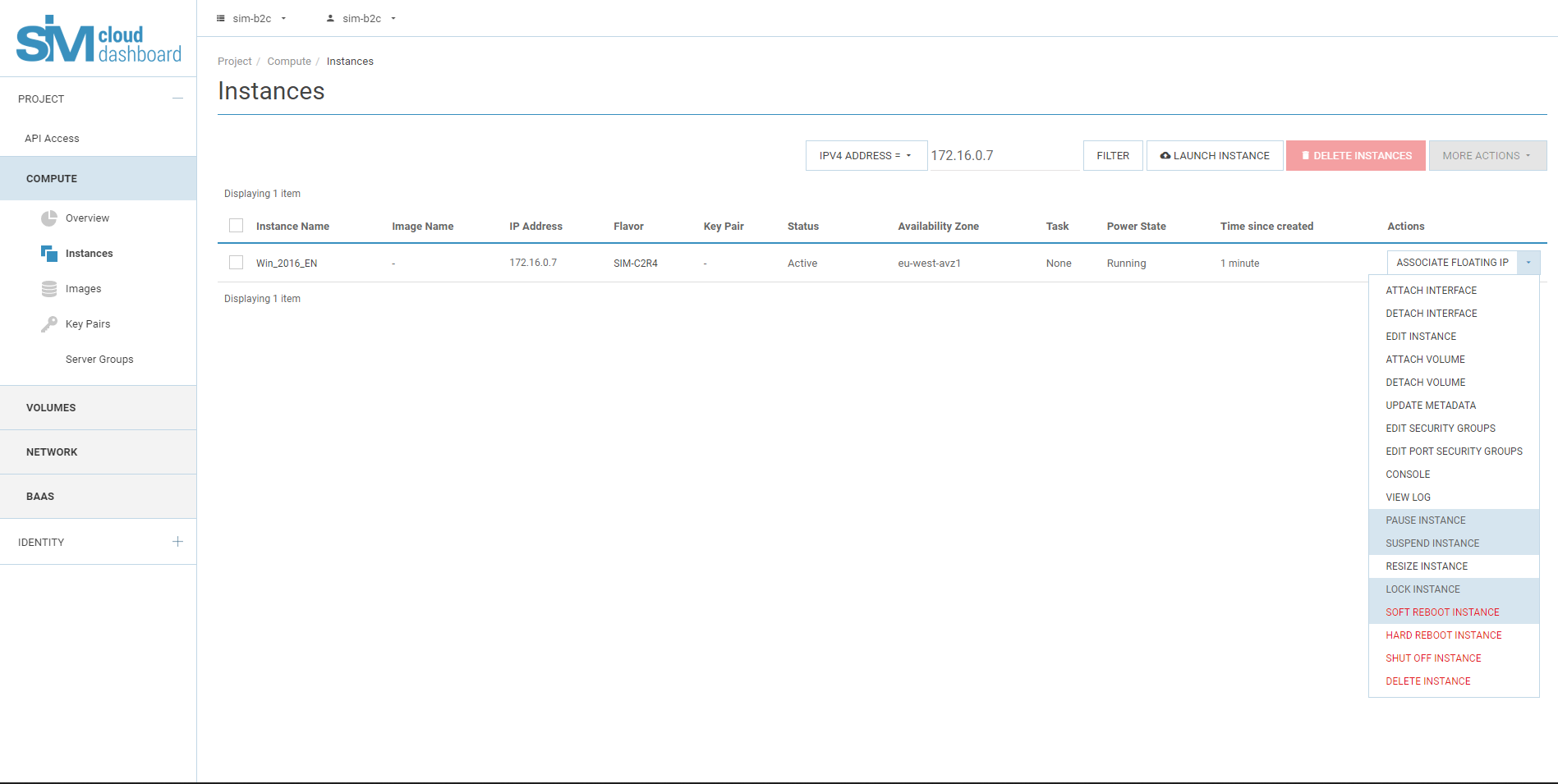
- Please note that only Windows instances require additional configuration after installation, Linux instances
- do not need additional actions and are immediately ready to work.
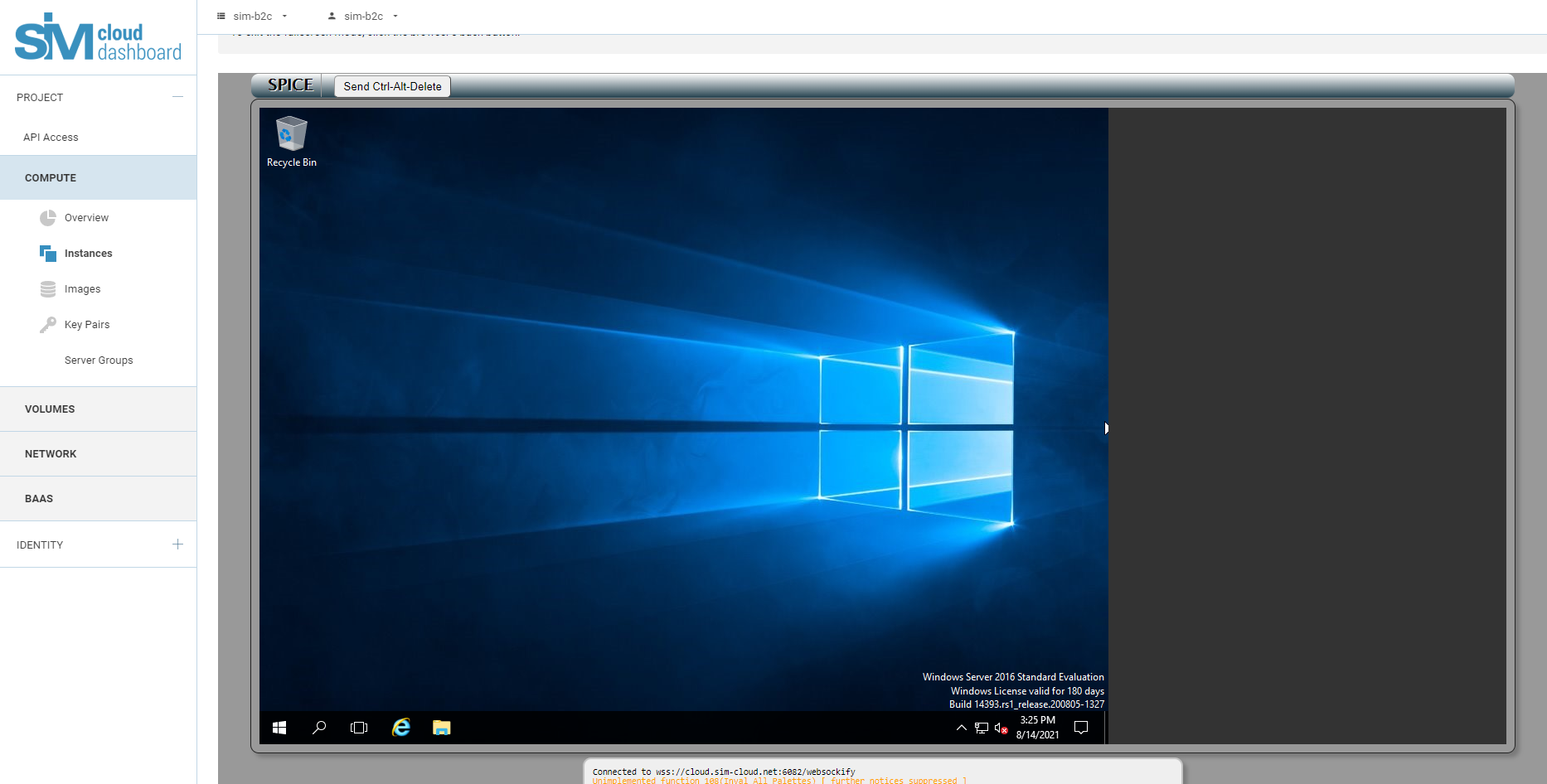
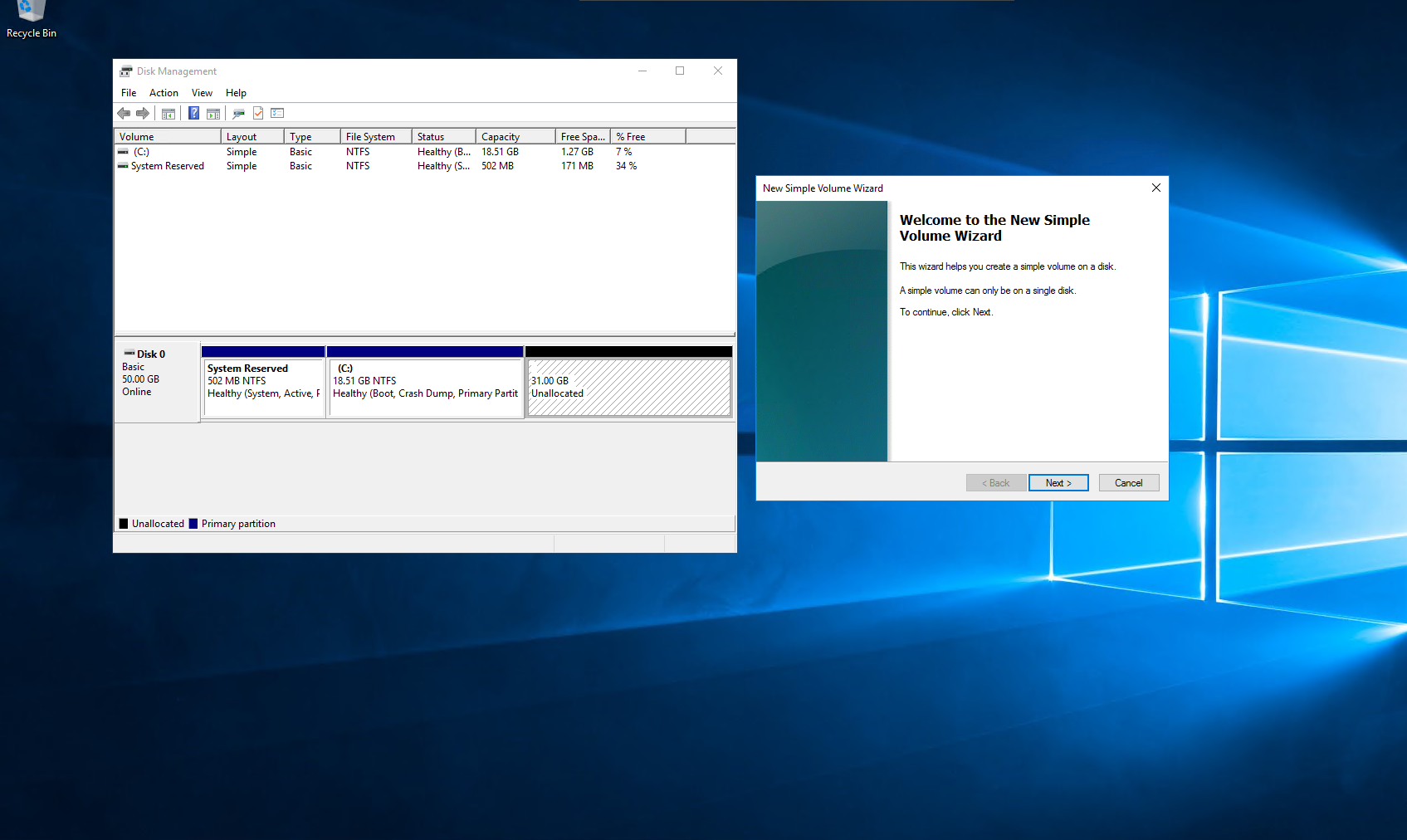
- When creating a disk that is larger than the minimum required volume, you must complete the procedure for expanding the disk using OS tools.
4.6. Checking network settings.
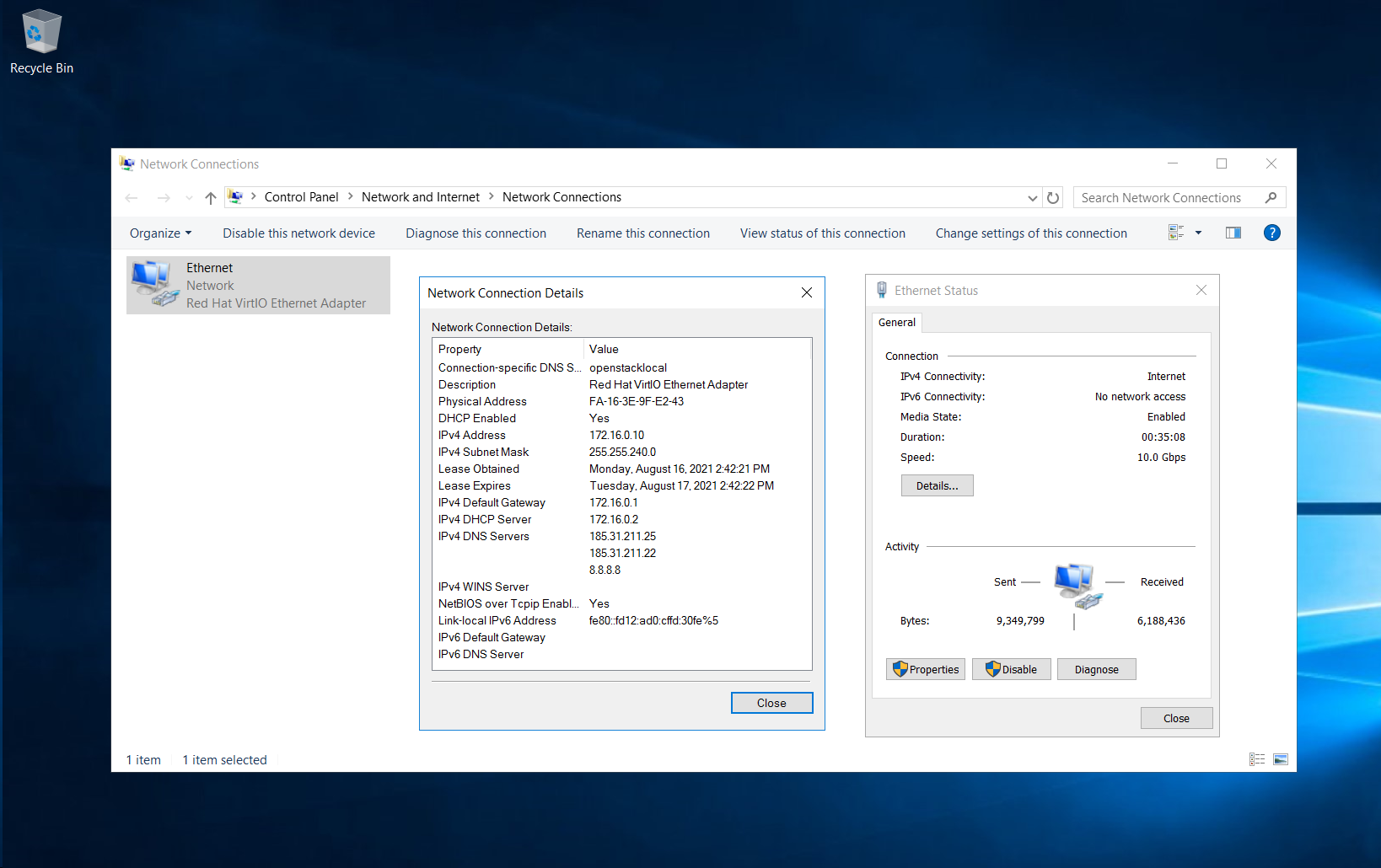
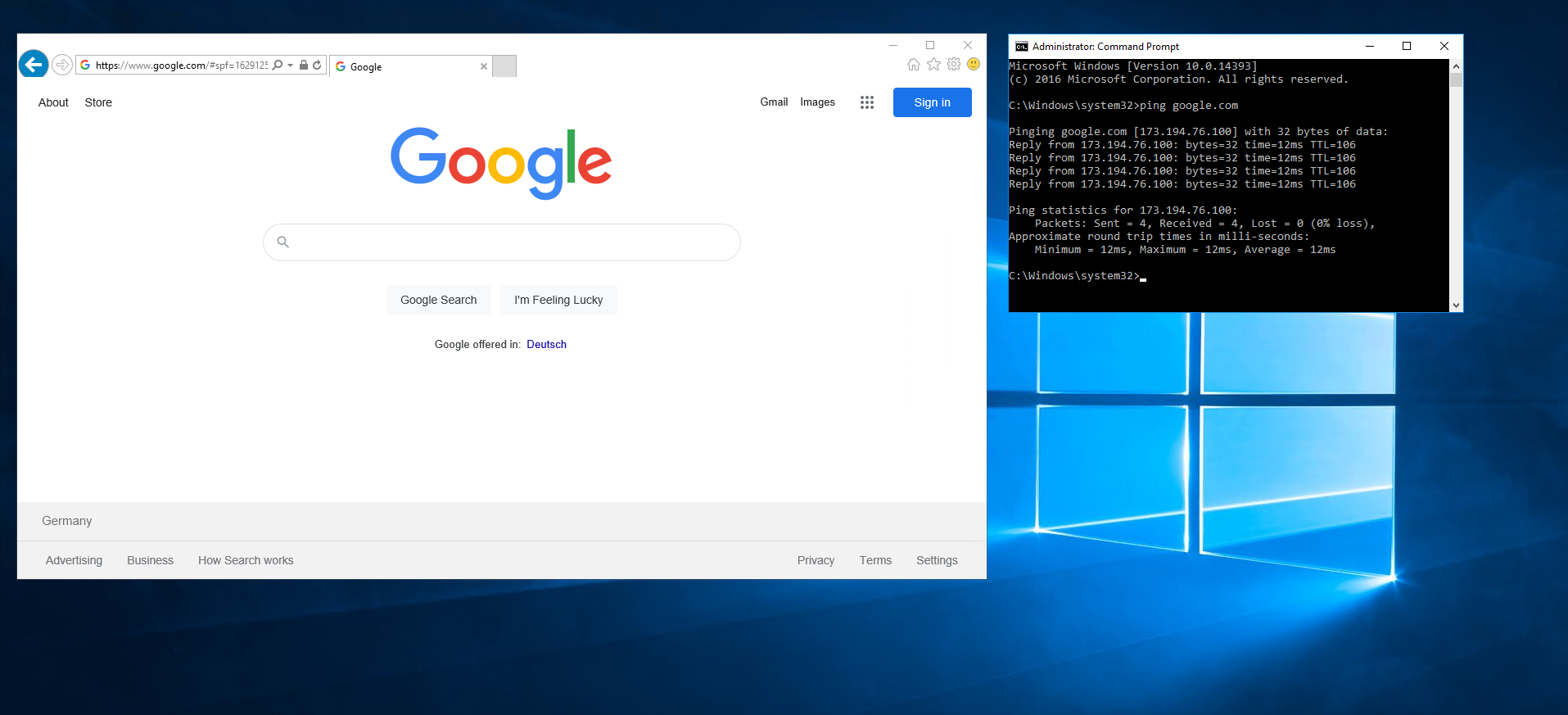
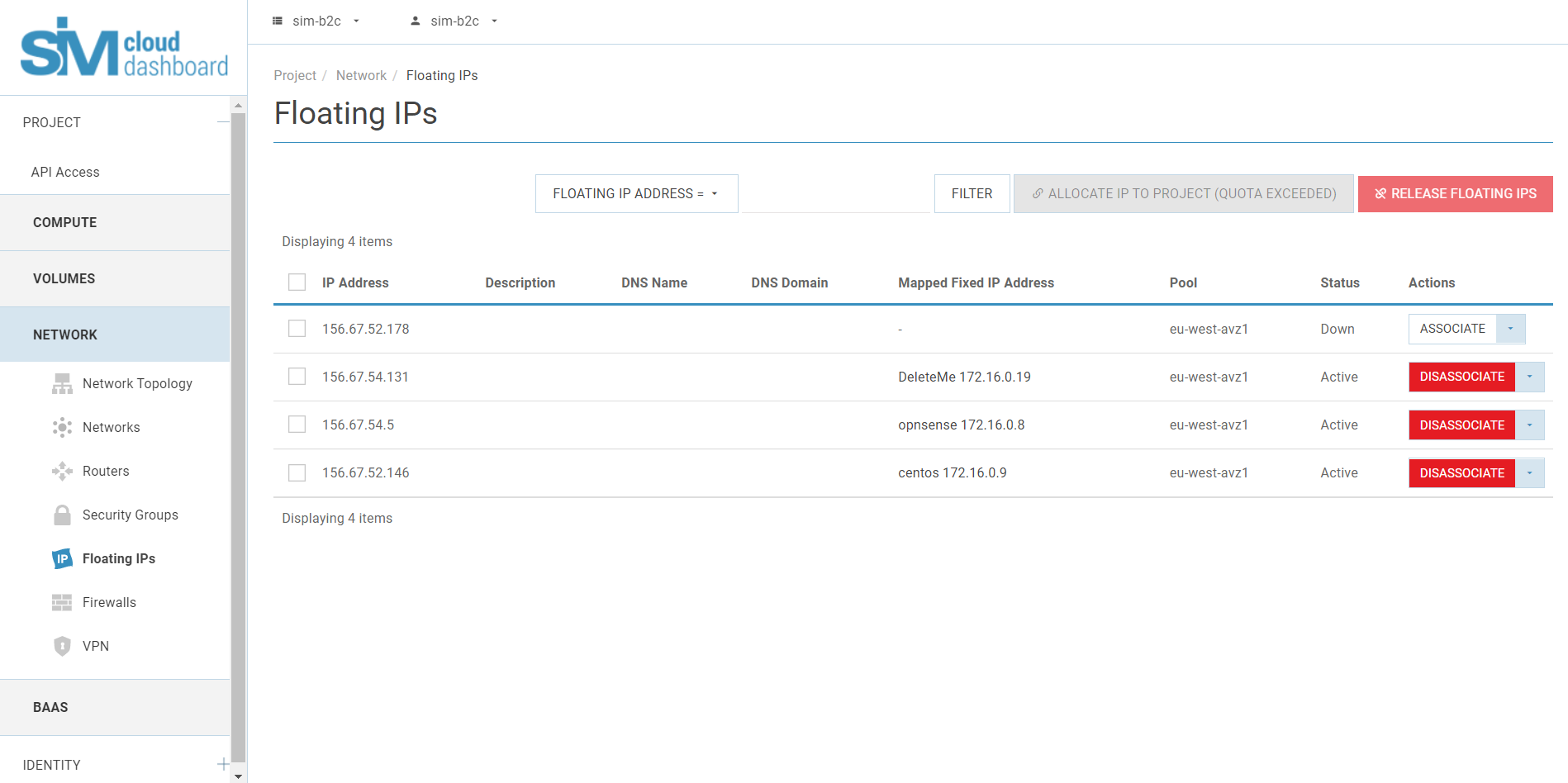
- Assigning a floating IP
In the Projects tab, select the Networking tab.
5.1. Go to the Floating IPs tab, which displays the floating
Instance-dedicated IP addresses.
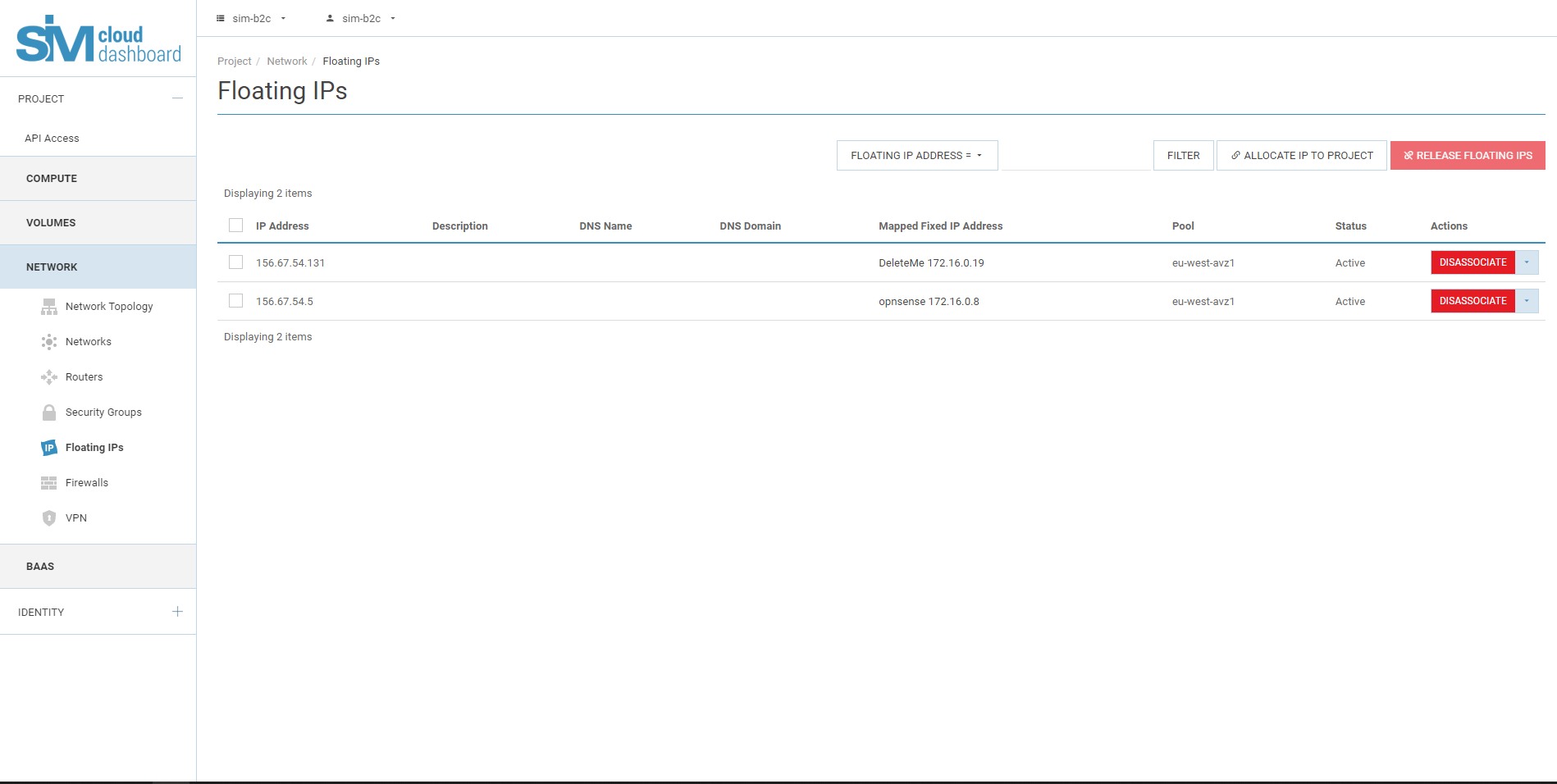
5.2. Click to "Allocate ip to project" button
5.3. Select the pool from which to select an IP address.
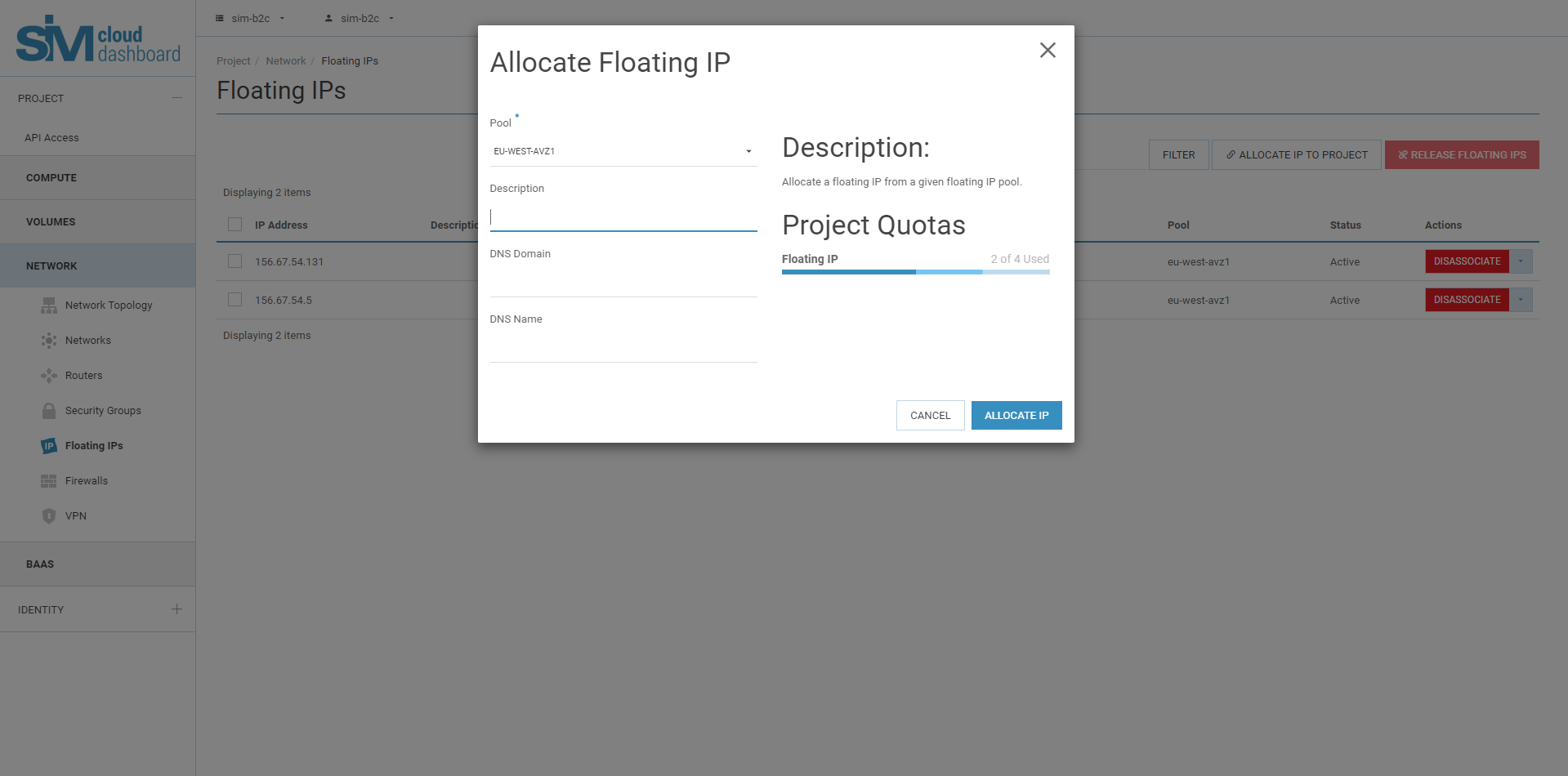
5.4. Click "Allocate IP".
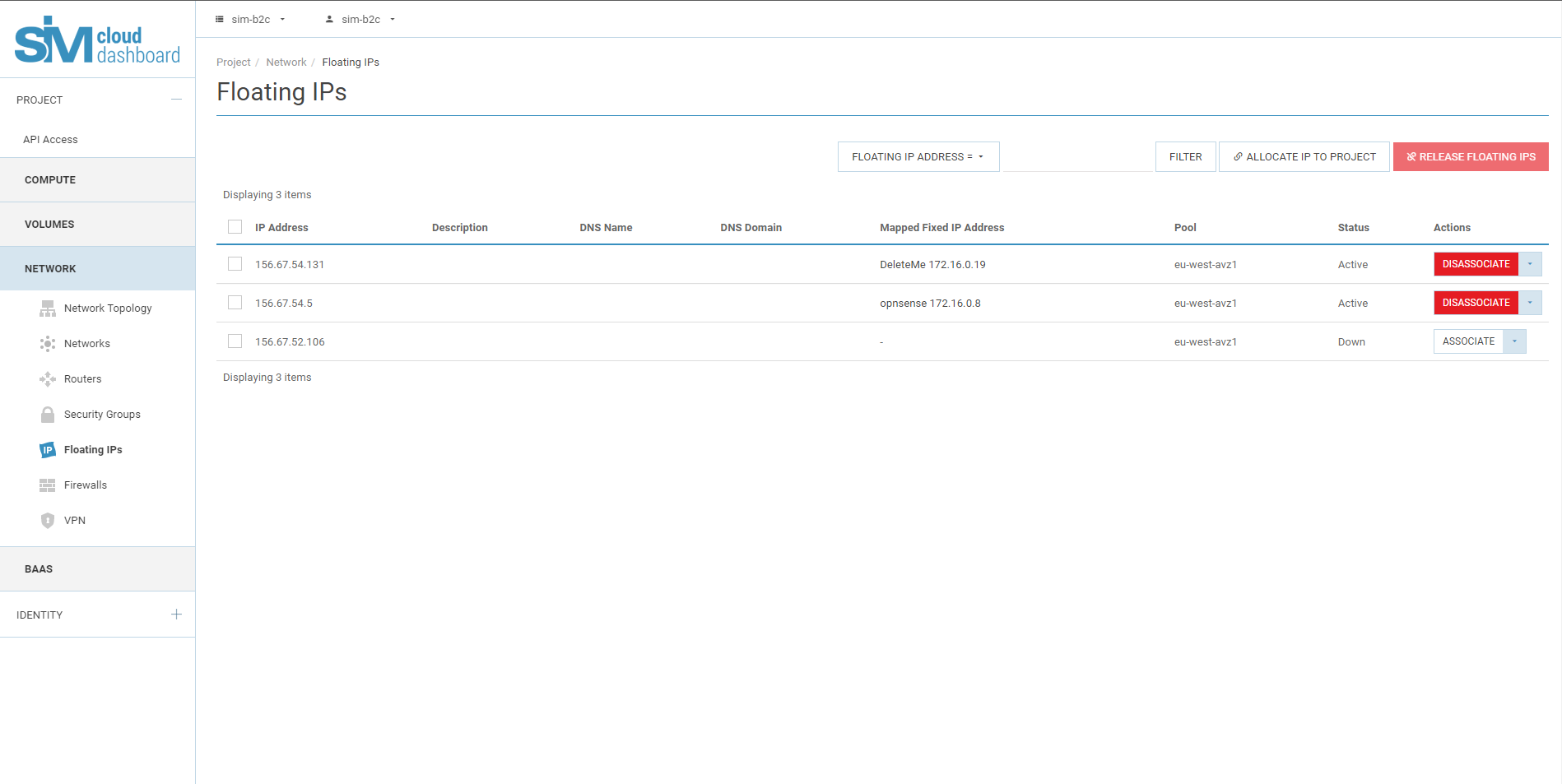
5.5. In the Floating IPs list, click Assign.
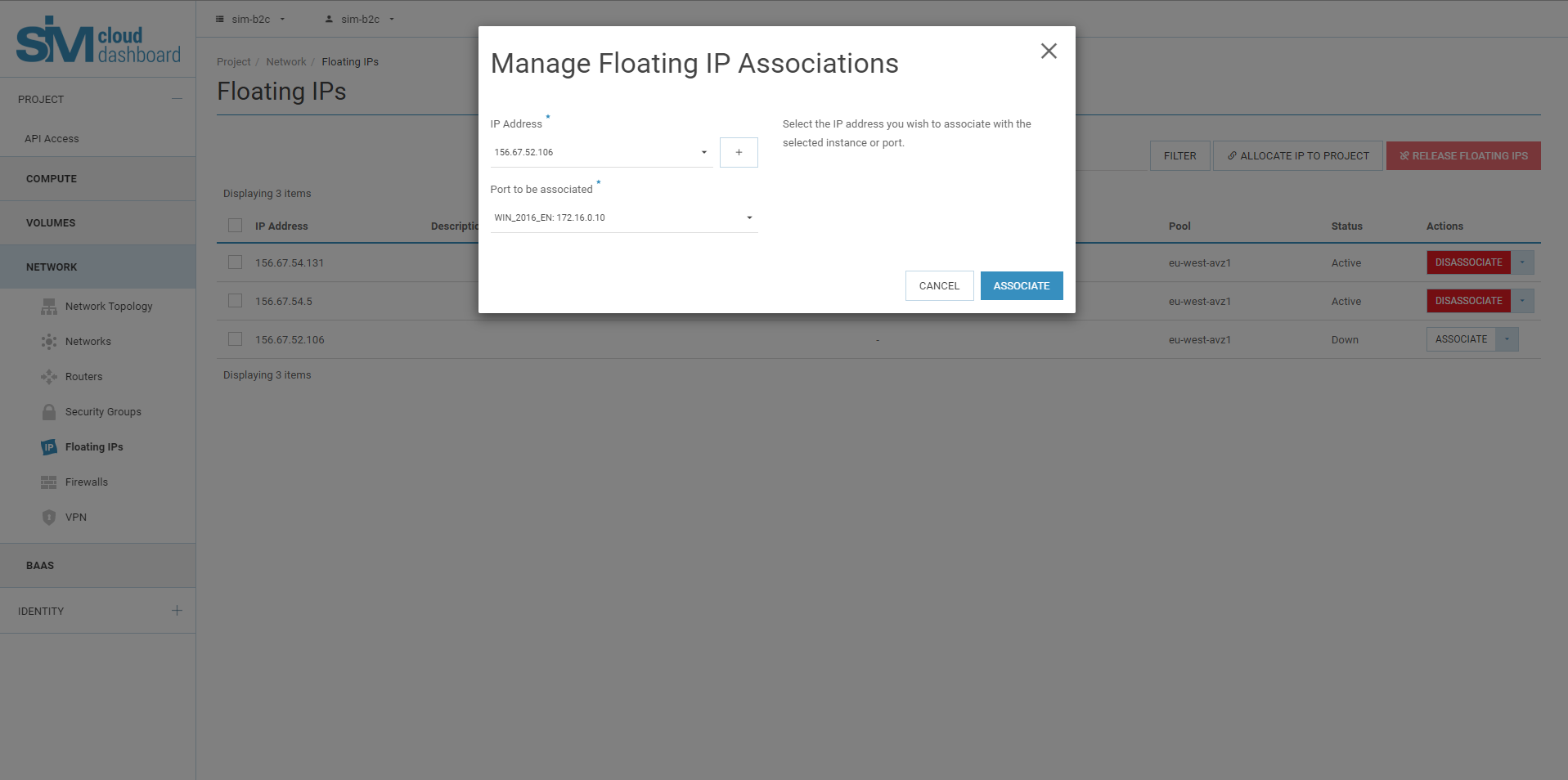
5.6. In the Manage Floating IP Assignment dialog box, select the following options:
The IP address field is filled in automatically, but you can add a new IP address by clicking the "+" button.
In the Destination Port field, select a port from the list.
The list displays all instances with fixed IP addresses that can be assigned a floating IP.
5.7. Click Assign.
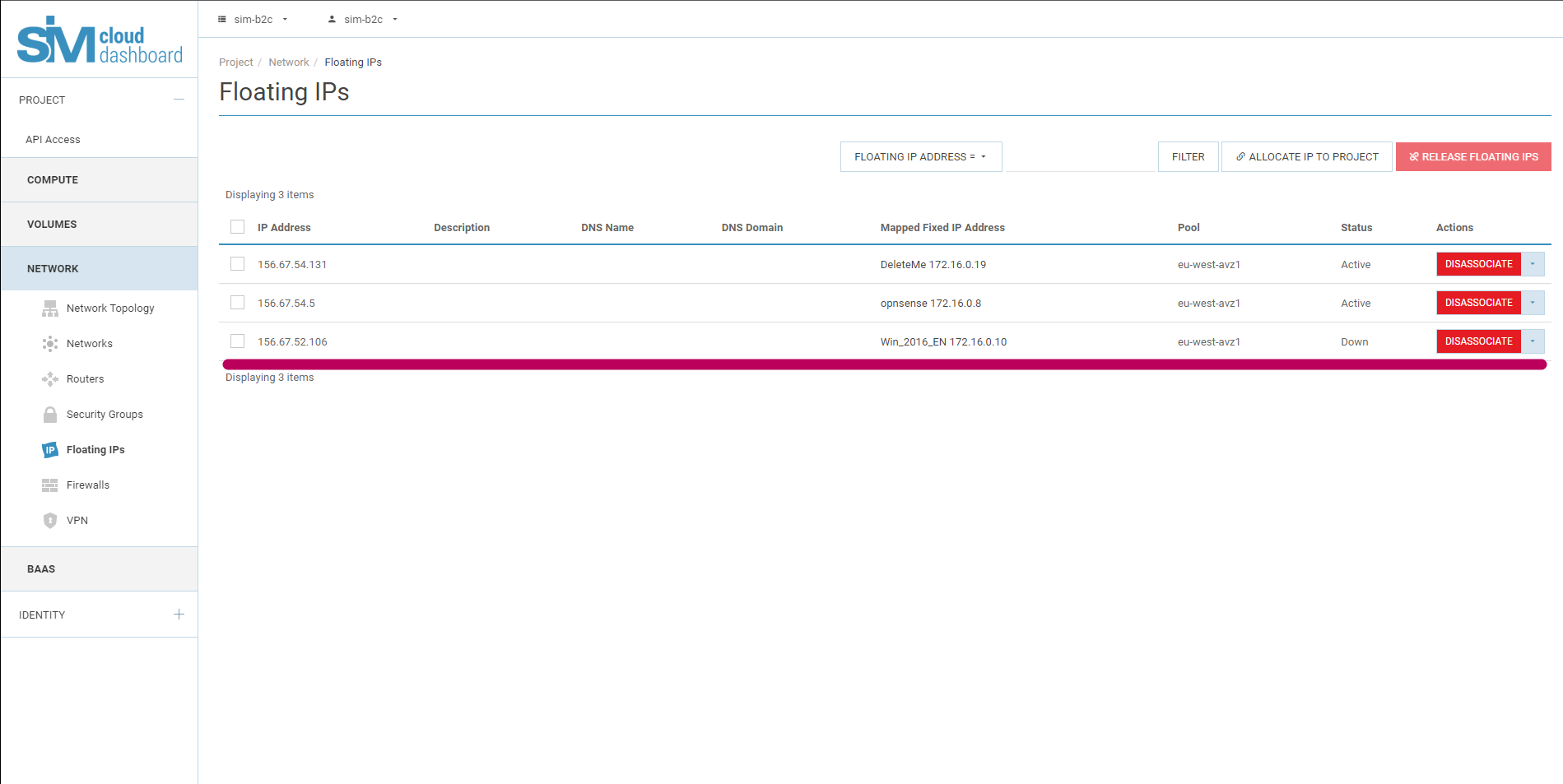
To unbind the IP address from the instance, click the Unassign button.
When a floating IP is assigned to an instance, you need to change group policies.
This step will allow you to finally open remote access to the instance from required IP addresses or subnets.
Changing security groups
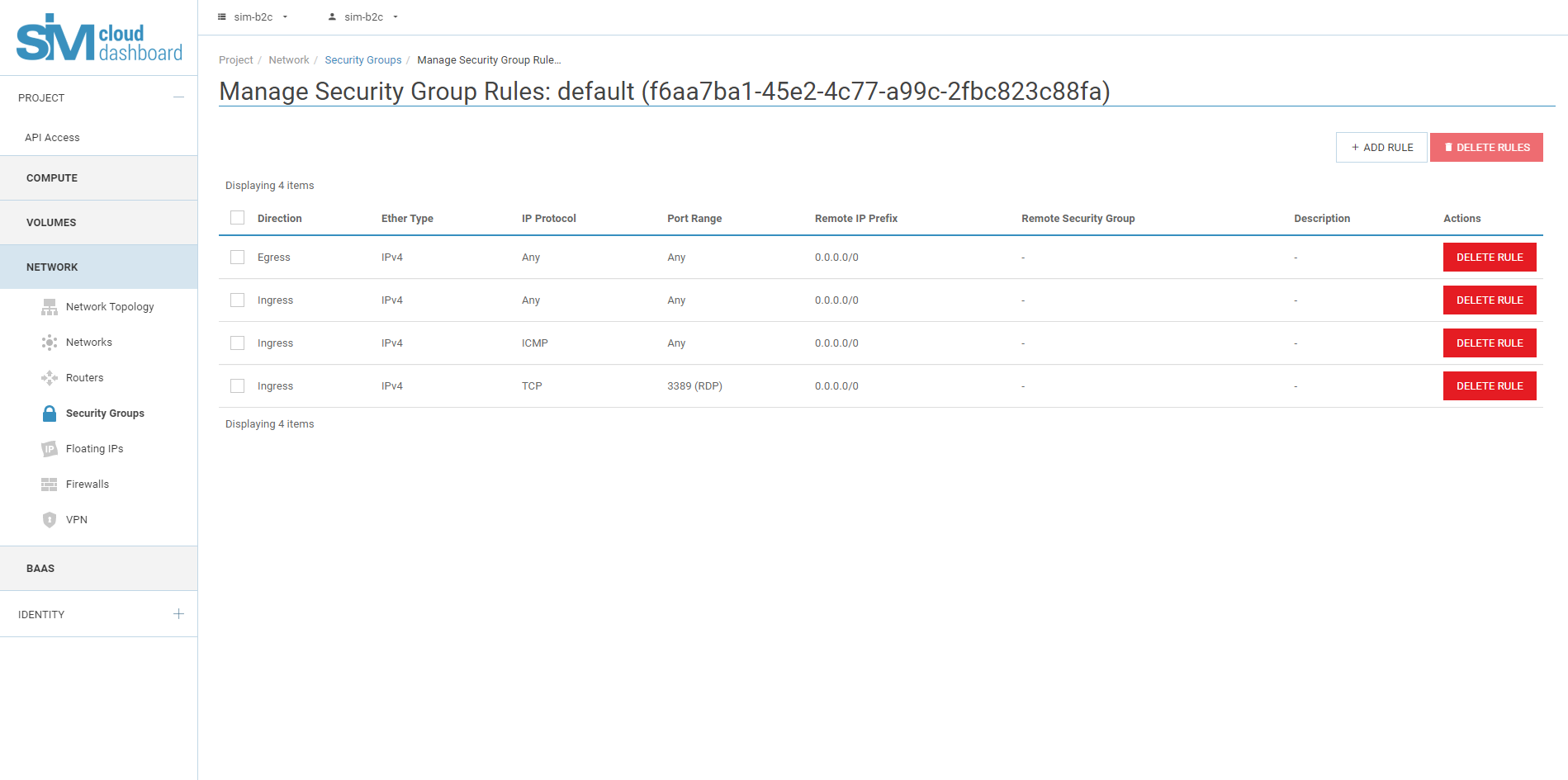
All outbound traffic is allowed on instance ports, and inbound traffic is blocked by the default security group.
This procedure includes access to the instance via RDP and ICMP (ping). The rules apply to all instances within a given project and must be installed for each project unless there is a reason to deny RDP or ICMP access for instances.
Adding a rule to the default security group:
6.1. На вкладке «Проект» откройте вкладку «Сеть».
On the Project tab, open the Networking tab.
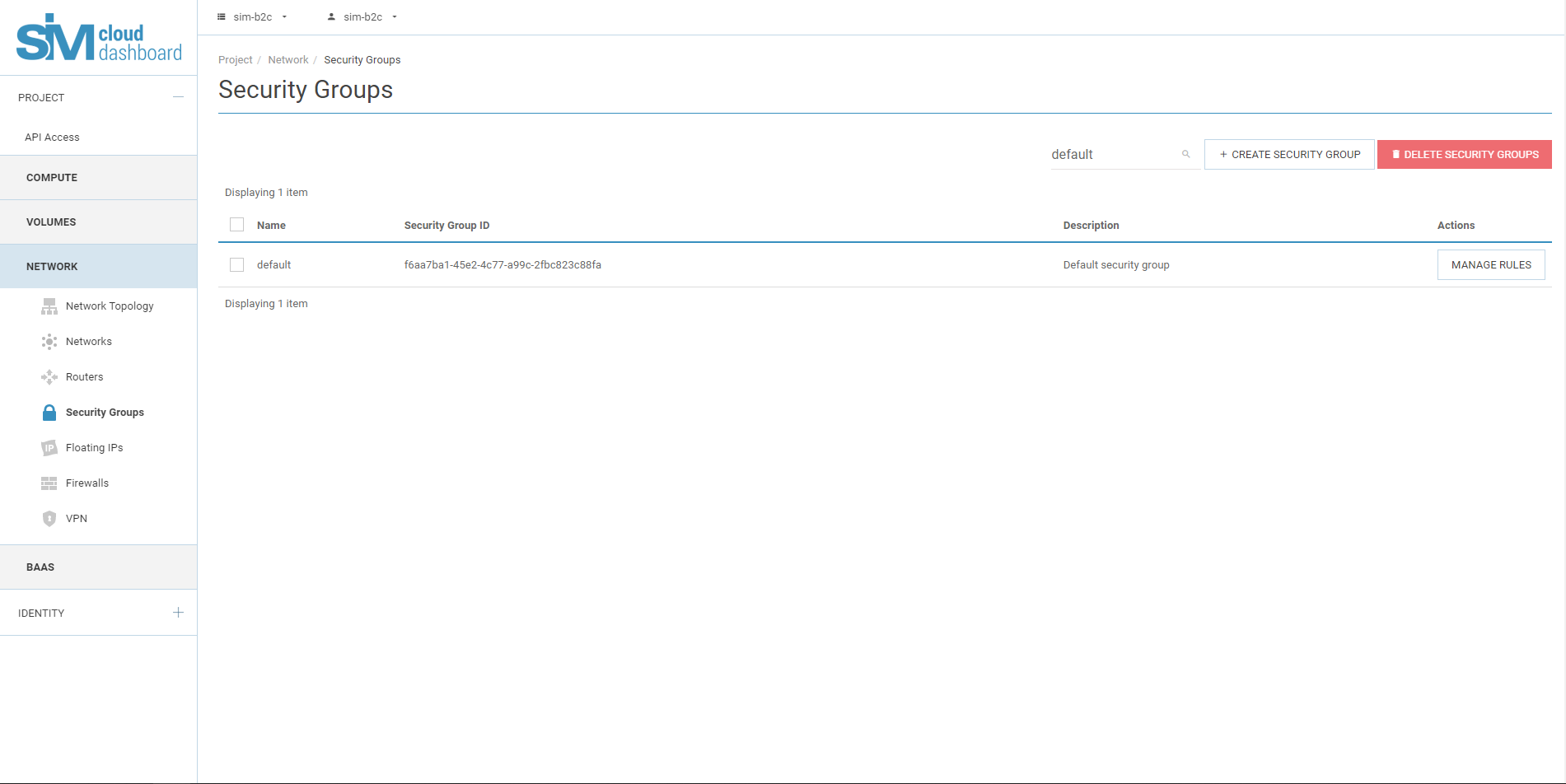
6.2. Select a default security group and click Manage Rules.
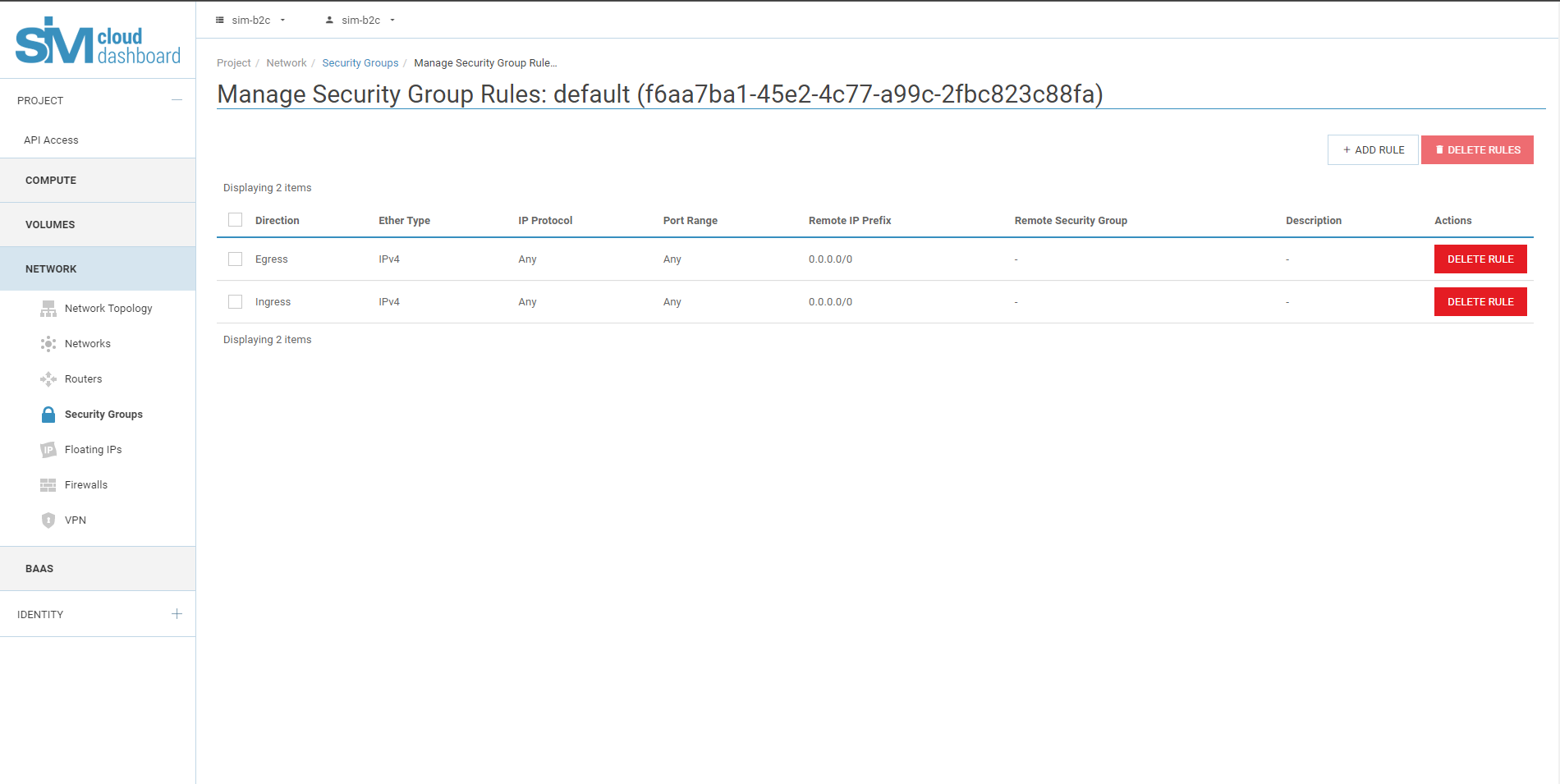
6.3. To allow RDP access, click Add Rule.
6.4. In the Add Rule dialog box, enter the following values:
Rule: RDP
Remote Address: CIDR
CIDR: 0.0.0.0/0
To accept requests from a specific range of IP addresses, enter a block of IP addresses in the CIDR field.
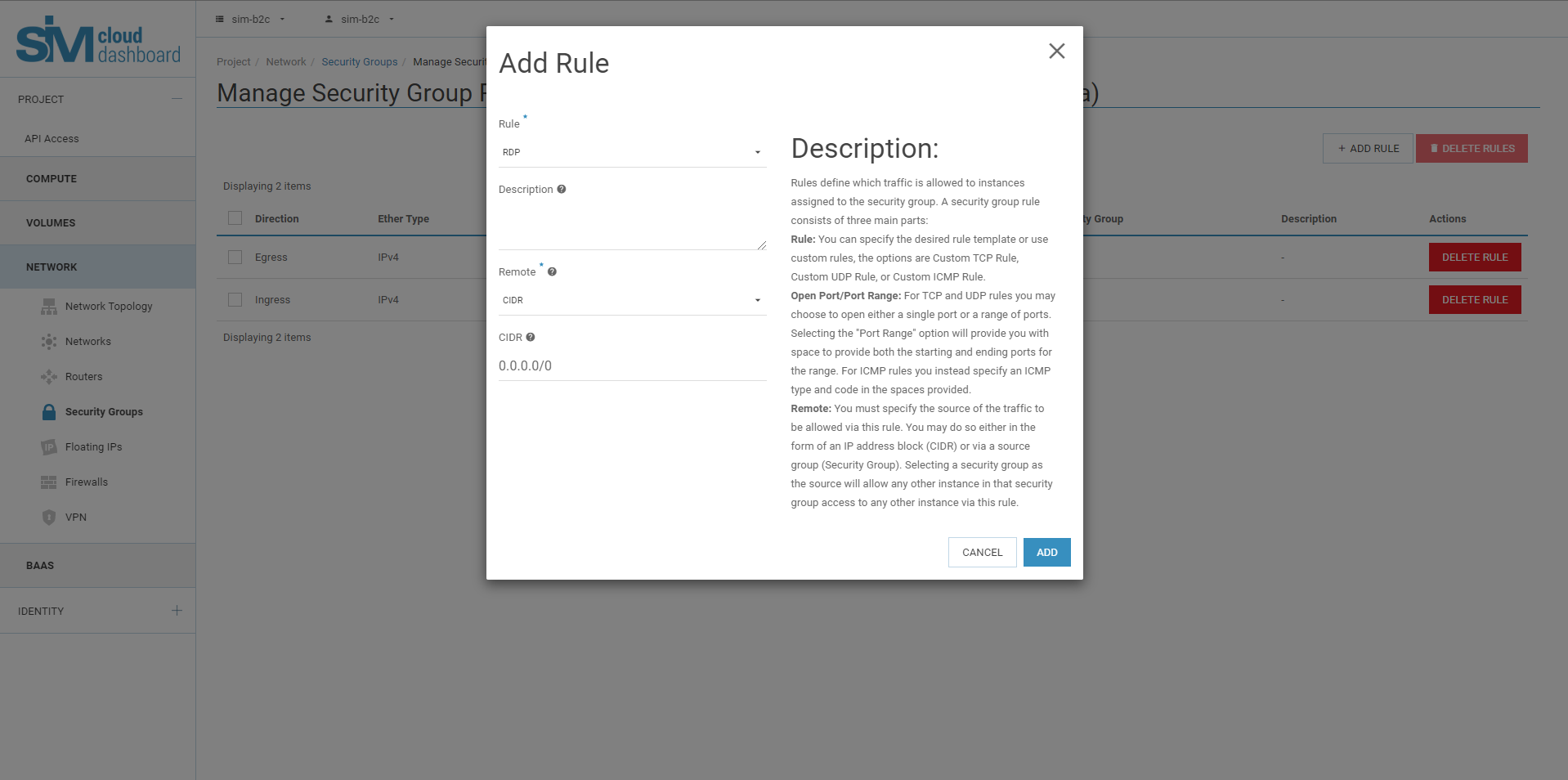
6.5. Click Add.
6.6. Now port 3389 RDP will be open on the port of the instance, for requests from any IP addresses.
6.7. To add an ICMP rule, click "Add Rule".
6.8. In the Add Rule dialog box, enter the following values:

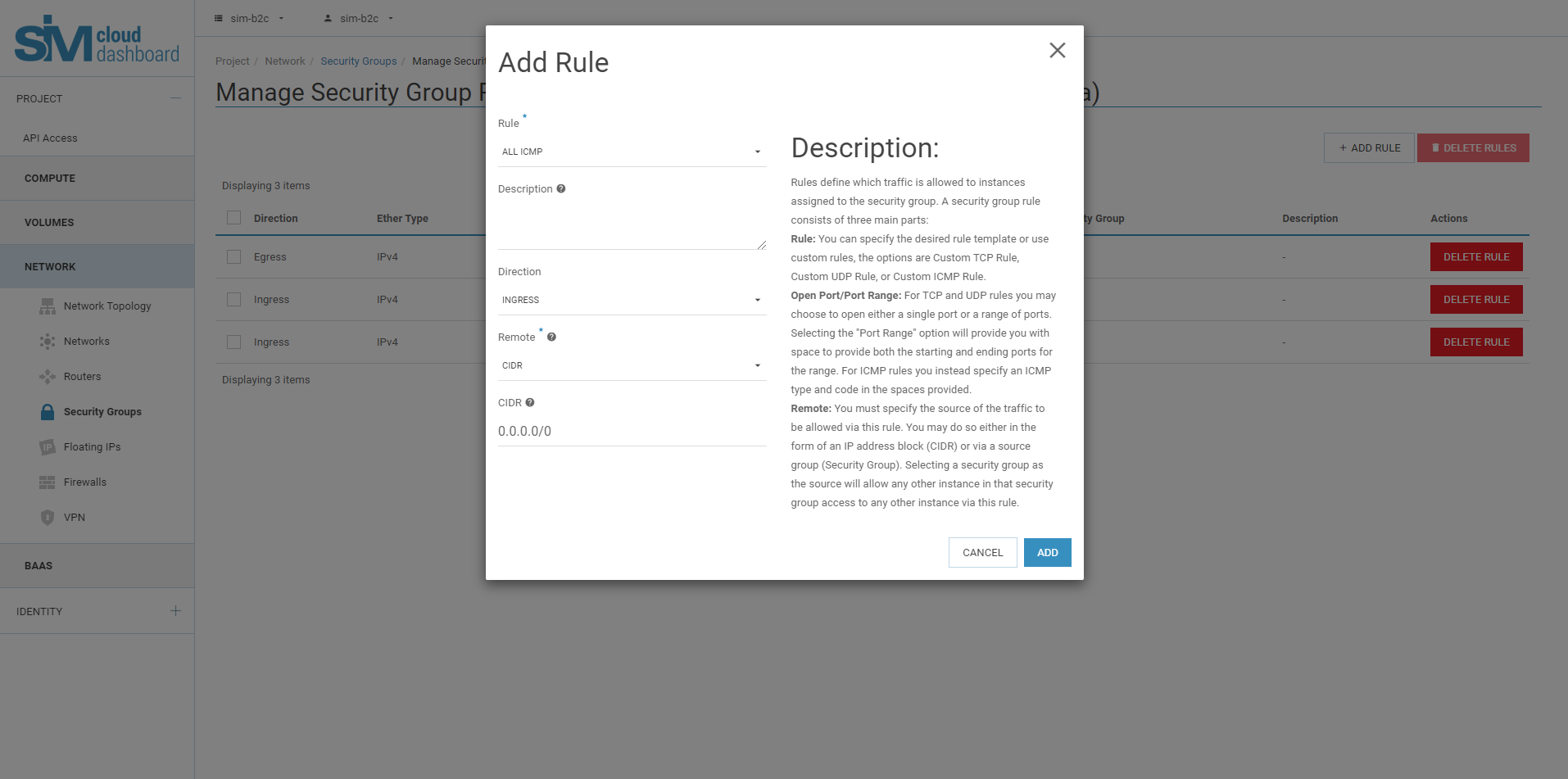
6.9. Click Add.
Instances will now accept all incoming ICMP packets. Additionally, for Windows instances, you must enable ICMP permissive rules.
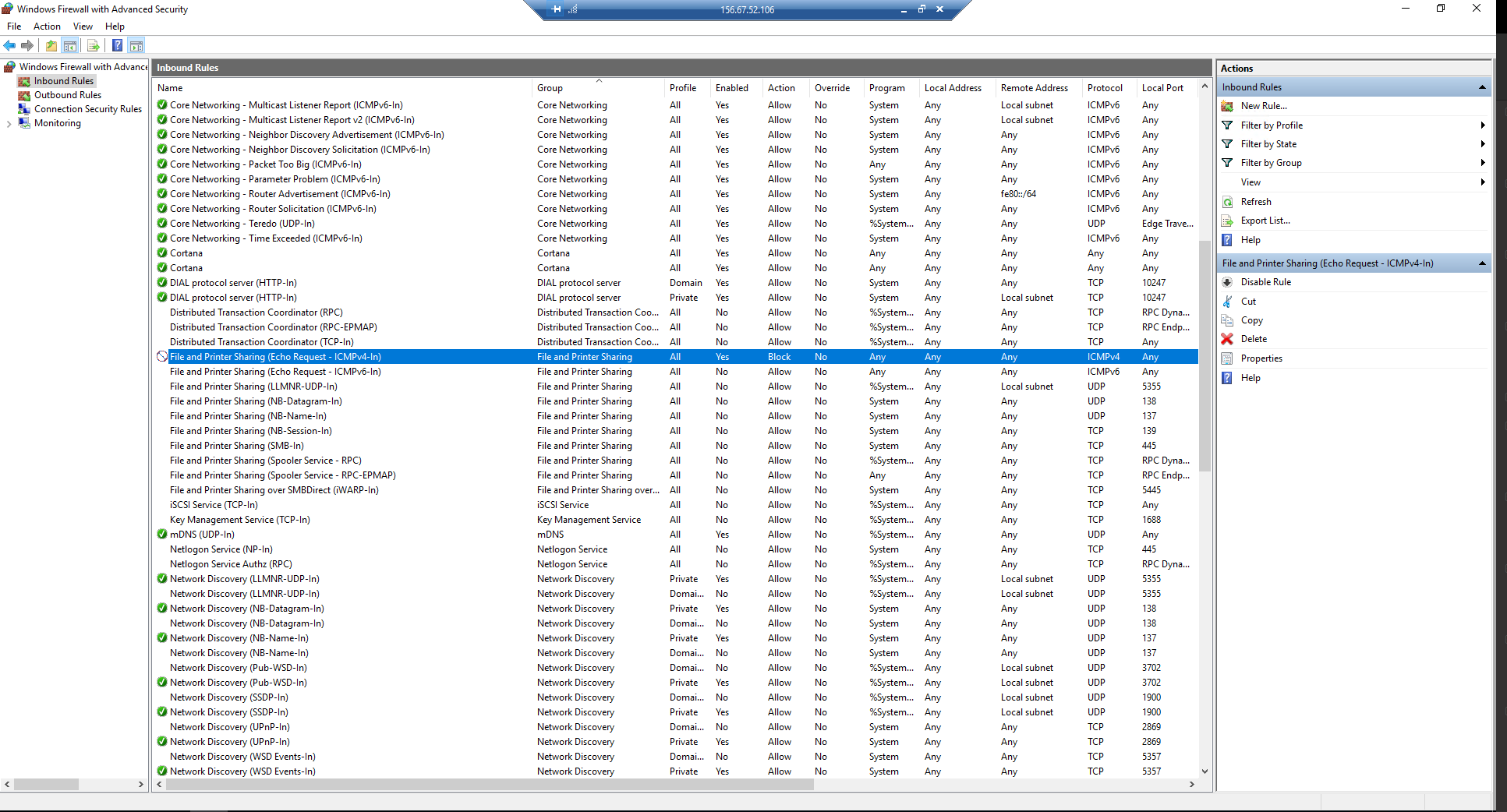
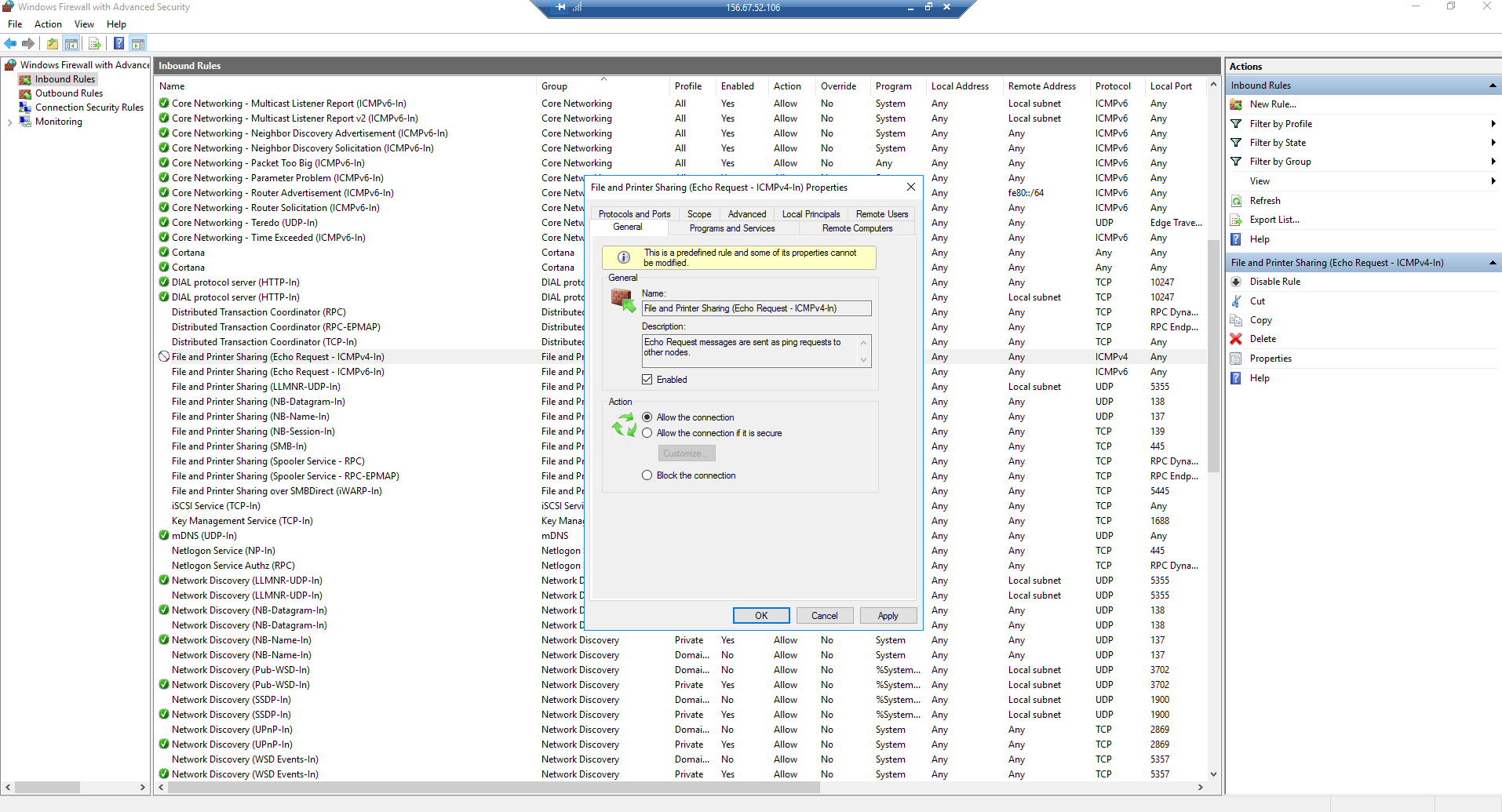
After you assign an IP address and configure the security group rules for the instance, it will become publicly available on the floating IP address from the public network.
- Exiting the SIM-Cloud dashboard
At the top of the window where your username is displayed, you must select the drop-down list and click “Logout”, after which you will be redirected to the login page.
Let’s summarize.
After studying this article, we can quickly create instances and configure access to them using security groups and floating IP.